Exposure-toxicity relationship of cabozantinib in patients with renal cell cancer and salivary gland cancer
- PMID: 34494665
- PMCID: PMC9291492
- DOI: 10.1002/ijc.33797
Exposure-toxicity relationship of cabozantinib in patients with renal cell cancer and salivary gland cancer
Abstract
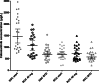
Cabozantinib is registered in fixed 60 mg dose. However, 46% to 62% of patients in the registration studies needed a dose reduction due to toxicity. Improved clinical efficacy has been observed in renal cell carcinoma patients (RCC) with a cabozantinib exposure greater than 750 μg/L. In our study we explored the cabozantinib exposure in patients with different tumour types. We included RCC patients from routine care and salivary gland carcinoma (SGC) patients from a phase II study with ≥1 measured Cmin at steady-state. The geometric mean (GM) Cmin at the starting dose, at 40 mg and at best tolerated dose (BTD) were compared between both tumour types. Forty-seven patients were included. All SGC patients (n = 22) started with 60 mg, while 52% of RCC patients started with 40 mg. GM Cmin at the start dose was 1456 μg/L (95% CI: 1185-1789) vs 682 μg/L (95% CI: 572-812) (P < .001) for SGC and RCC patients, respectively. When dose-normalised to 40 mg, SGC patients had a significantly higher cabozantinib exposure compared to RCC patients (Cmin 971 μg/L [95% CI: 790-1193] vs 669 μg/L [95% CI: 568-788]) (P = .005). Dose reductions due to toxicity were needed in 91% and 60% of SGC and RCC patients, respectively. Median BTD was between 20 to 30 mg for SGC and 40 mg for RCC patients. GM Cmin at BTD were comparable between the SGC and the RCC group, 694 μg/L (95% CI: 584-824) vs 583 μg/L (95% CI: 496-671) (P = .1). The observed cabozantinib exposure at BTD of approximately 600 μg/L is below the previously proposed target. Surprisingly, a comparable exposure at BTD was reached at different dosages of cabozantinib for SGC patients compared to RCC patients Further research is warranted to identify the optimal exposure and starting dose to balance efficacy and toxicity.
Keywords: cabozantinib; pharmacokinetics; renal cell carcinoma; salivary gland neoplasms; toxicity.
© 2021 The Authors. International Journal of Cancer published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of UICC.
Conflict of interest statement
All mentioned relationships are outside the submitted work. FGAJ has been on an advisory board for Amgen and Genzyme. IMED received a research grant from Novartis. NPvE has received research grants from Novartis, Astellas, Janssen‐Cilag, Pfizer, Ipsen, has been on an advisory board for Pfizer, and received honoraria from Bayer and Sanofi. CMLvH has received research grants form AstraZeneca, Bristol Meyers Squibb, Merck Sharp and Dohme, Merck, Ipsen, Sanofi, and Novartis, has been on an advisory board for Bayer, Bristol‐Meyers Squibb, Ipsen, Merck Sharp and Dohme and Regeneron. SFM received honoraria from Pfizer, Roche and Merck Sharp and Dohme and Bristol Meyers Squibb. The other authors declare no conflicts of interest. (SDK, MU, WvB).
Figures
References
-
- Yakes FM, Chen J, Tan J, et al. Cabozantinib (XL184), a novel MET and VEGFR2 inhibitor, simultaneously suppresses metastasis, angiogenesis, and tumor growth. Mol Cancer Ther. 2011;10(12):2298‐2308. - PubMed
-
- Bergerot P, Lamb P, Wang E, Pal SK. Cabozantinib in combination with immunotherapy for advanced renal cell carcinoma and urothelial carcinoma: rationale and clinical evidence. Mol Cancer Ther. 2019;18(12):2185‐2193. - PubMed
-
- FDA . Cabometyx prescribing information. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/208692s008lbl.pdf. Accessed December 1, 2020.
-
- Choueiri TK, Powles T, Burotto M, et al. 696O_PR Nivolumab + cabozantinib vs sunitinib in first‐line treatment for advanced renal cell carcinoma: first results from the randomized phase III CheckMate 9ER trial. Ann Oncol. 2020;31:S1159.
-
- Agarwal N, Vaishampayan U, Green M, et al. 872P: phase Ib study (COSMIC‐021) of cabozantinib in combination with atezolizumab: results of the dose escalation stage in patients (pts) with treatment‐naïve advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC). Ann Oncol. 2018;29:viii308.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

