Emergence of blaNDM-1 and blaVIM producing Gram-negative bacilli in ventilator-associated pneumonia at AMR Surveillance Regional Reference Laboratory in India
- PMID: 34495985
- PMCID: PMC8425556
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0256308
Emergence of blaNDM-1 and blaVIM producing Gram-negative bacilli in ventilator-associated pneumonia at AMR Surveillance Regional Reference Laboratory in India
Abstract
Introduction: Ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP) may be a life threatening nosocomial infection encountered in intensive care units. Currently the emergence of carbapenem-resistant Gram-negative pathogens has become worrisome threat worldwide.
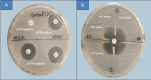
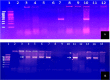
Material and methods: Endotracheal aspirates samples were collected from patients who were under mechanical ventilation for > 48 h. The bacterial isolates were identified by MALDI-TOF-MS and antibiotic susceptibility testing performed. All carbapenem resistant isolates were tested by Modified Hodge test (MHT), modified carbapenem inactivation method (mCIM), and EDTA-CIM (eCIM) and PCR were performed to detect blaIMP, blaVIM and blaNDM producing MBL genes.
Results: VAP occurred in 172/353(48.7%), 23.3% had early-onset VAP and 76.7% had late-onset VAP. Males (69.2%) were found to suffer more from VAP. Prior antibiotic therapy, CPI>6, prior surgery and tracheostomy were associated with VAP. The mortality in VAP (58.1%) contrasted with non-VAP (40%). 99/169 (58.6%) Gram-negative isolates were resistant to carbapenems. Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Klebsiella pneumoniae were common pathogens found in late onset VAP, whereas K. pneumoniae, A. baumannii and Staphylococcus aureus were common in early onset VAP. The PCR results detected blaNDM in 37/172(21.5%) and blaVIM in 30/172(17.4%); 15/172(8.7%) isolates carried both genes.
Conclusion: The blaNDM-1 and blaVIM genes are the main antibiotic-resistance genes that induce resistance patterns to carbapenems in VAP, highlighting CRE strains of potential public health concern and therapeutic challenge. Diagnostic laboratories in India must get on high caution for early MBL detection as it may limit the wide dispersal of MBL genes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Chastre Jean, Luyt Charles-Edouard, Murray and Nadel’s Textbook of Respiratory Medicine (Sixth Edition), Elsevier Saunders; 2016.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

