Formulation and Evaluation of Enteric Coated Elementary Osmotic Tablets of Aceclofenac
- PMID: 34496557
- PMCID: PMC8430416
- DOI: 10.4274/tjps.galenos.2020.03443
Formulation and Evaluation of Enteric Coated Elementary Osmotic Tablets of Aceclofenac
Abstract
Objectives: This study aimed to develop a controlled drug delivery device for aceclofenac, a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug. Therefore, the agent was projected to develop an osmotic pump with enteric coating. The strength of the semipermeable membrane was improved by optimizing the formulation of the device, which can control the drug release over a prolonged period of time.
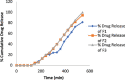
Materials and methods: The formulations were designed and optimized by using the statistical design of experiment followed by 32 factorial design to discover the best formulation. Several evaluation tests were performed to assess the physical parameters of the formulations. The percentage drug release of the formulations was observed for up to 9 h.
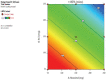
Results: The model 3D graph analysis indicated that as an osmogen, a higher percentage of potassium chloride was utilized more effectively than mannitol for the rapid dissolution of osmotic tablets. The optimized formulation can release 88.60±0.02% up to 9 h. The accelerated stability study confirmed that the optimized formulation was stable.
Conclusion: The formulated osmotic tablets of aceclofenac were therapeutically safe and effective and did not release any drug content in the simulated gastric medium for a predetermined time.
Keywords: 32 factorial design; 3D graph analysis; Statistical design of experiment; osmotic tablet.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
Formulation design and characterization of an elementary osmotic pump tablet of flurbiprofen.PDA J Pharm Sci Technol. 2014 Jul-Aug;68(4):333-46. doi: 10.5731/pdajpst.2014.00984. PDA J Pharm Sci Technol. 2014. PMID: 25035256
-
Development of controlled release osmotic pump tablet of glipizide solid dispersion.Curr Drug Deliv. 2014;11(6):817-27. doi: 10.2174/15672018113109990040. Curr Drug Deliv. 2014. PMID: 23859357
-
Development, evaluation, and influence of formulation and process variables on in vitro performance of oral elementary osmotic device of atenolol.Int J Pharm Investig. 2016 Oct-Dec;6(4):238-246. doi: 10.4103/2230-973X.195951. Int J Pharm Investig. 2016. PMID: 28123994 Free PMC article.
-
Development and evaluation of microporous osmotic tablets of diltiazem hydrochloride.J Adv Pharm Technol Res. 2012 Apr;3(2):124-9. doi: 10.4103/2231-4040.97292. J Adv Pharm Technol Res. 2012. PMID: 22837961 Free PMC article.
-
Formulation development and optimization of bilayer tablets of aceclofenac.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2012 Sep;9(9):1041-50. doi: 10.1517/17425247.2012.707187. Epub 2012 Jul 12. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2012. PMID: 22788786
References
-
- Mothilal M, Swati PS, Nelofar S, Damodharan N, Manimaran V, Lakshmi KS. Formulation and evaluation of aceclofenac compression coated tablets for colon drug delivery. Res J Pharm Biol Chem Sci. 2012;3:1062–1071.
-
- Roco MC, Bainbridge WS. Societal implications of nanoscience and nanotechnology: maximizing human benefit. J Nanoparticle Res. 2005;7:1–13.
-
- Ahuja N, Kumar V, Rathee P. Osmotic-controlled release oral delivery system: An advanced oral delivery form. Pharm Innov. 2012;1:116–124.
-
- Rathore GS, Gupta RN. Formulation development and evaluation of controlled porosity osmotic pump delivery system for oral delivery of atenolol. Asian J Pharm. 2012;6:151–160.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
