Effect of bioimpedance-defined overhydration parameters on mortality and cardiovascular events in patients undergoing dialysis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 34496645
- PMCID: PMC8438275
- DOI: 10.1177/03000605211031063
Effect of bioimpedance-defined overhydration parameters on mortality and cardiovascular events in patients undergoing dialysis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the role of bioimpedance-defined overhydration (BI-OH) parameters in predicting the risk of mortality and cardiovascular (CV) events in patients undergoing dialysis.
Methods: We searched multiple electronic databases for studies investigating BI-OH indicators in the prediction of mortality and CV events through 23 May 2020. We assessed the effect of BI-OH indexes using unadjusted hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Sensitivity analysis was used for each outcome.
Results: We included 55 studies with 104,758 patients in the meta-analysis. Extracellular water/total body water (ECW/TBW) >0.4 (HR 5.912, 95% CI: 2.016-17.342), ECW/intracellular water (ICW) for every 0.01 increase (HR 1.041, 95% CI: 1.031-1.051), and OH/ECW >15% (HR 2.722, 95% CI: 2.005-3.439) increased the risk of mortality in patients receiving dialysis. ECW/TBW >0.4 (HR 2.679, 95% CI: 1.345-5.339) and ECW/ICW per increment of 10% (HR 1.032, 95% CI: 1.017-1.047) were associated with an increased risk of CV events in patients undergoing dialysis. A 1-degree increase in phase angle was a protective factor for both mortality (HR 0.676, 95% CI: 0.474-0.879) and CV events (HR 0.736, 95% CI: 0.589-0.920).
Conclusions: BI-OH parameters might be independent predictors for mortality and CV events in patients undergoing dialysis.
Keywords: Bioimpedance-defined overhydration; cardiovascular event; dialysis; meta-analysis; mortality; outcome.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
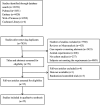
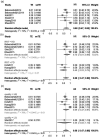

References
-
- US Renal Data System 2019 Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of Kidney Disease in the United States. Am J Kidney Dis 2019: S0272-6386(19)31008-X. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2019.09.002. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

