Transvaginal natural orifice specimen extraction surgery (NOSES) in 3D laparoscopic partial or radical nephrectomy: a preliminary study
- PMID: 34496814
- PMCID: PMC8424808
- DOI: 10.1186/s12894-021-00890-9
Transvaginal natural orifice specimen extraction surgery (NOSES) in 3D laparoscopic partial or radical nephrectomy: a preliminary study
Abstract
Background: With the development of minimally invasive technology, more and more people pay attention to aesthetics of the wound after operation. This study is aim to introduce a new surgical technique of transvaginal natural orifice specimen extraction surgery (NOSES) in 3D laparoscopic partial or radical nephrectomy and evaluate the safety, feasibility and clinical effect.
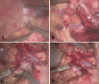
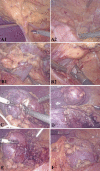
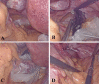
Methods: Eleven patients who underwent 3D laparoscopic partial nephrectomy (n = 7) or radical nephrectomy (n = 4) and NOSES were included in this study. The surgical procedures and techniques, especially the NOSES operation, are reported in detail. In addition, the basic clinical data, perioperative related data, perioperative complications were analyzed.
Results: All 11 patients were performed successfully without conversion to open surgery. The mean total operative time was 133 (84, 150) min. NOSES time was 15 (13, 16) min, and the postoperative hospital stay was 5 (5, 5) d. The mean visual analogue score (VAS) was 3 (2, 4) point and 1 (0, 1) point at 24 h and 48 h after operation, respectively. No patient had recurrence, metastasis and death during the follow-up period of 3 to 17 months. The median Vancouver Scar Scale (VSS) was 1 (1, 1) point. The mean of Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI) was 21.60 (20.20, 21.60), 21.80 (19.80, 21.80) respectively between preoperative and postoperative 3 months, which has no statistical difference (P = 0.179). There was no statistical difference in the Pelvic Floor Distress Inventory-short form 20 (PFDI-20) score between preoperative and postoperative 3 months (P = 0.142).
Conclusions: Transvaginal NOSES is safe and feasible in 3D laparoscopic partial or radical nephrectomy. Furthermore, it results in low incision-related pain without affecting the pelvic floor and sexual function.
Keywords: Laparoscopy; Natural orifice specimen extraction surgery (NOSES); Partial nephrectomy; Radical nephrectomy; Renal carcinoma.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A new and practical surgical technique of transvaginal natural orifice specimen extraction surgery (NOSES) in laparoscopic nephroureterectomy-an initial clinical experience.J Surg Oncol. 2021 Dec;124(7):1200-1206. doi: 10.1002/jso.26608. Epub 2021 Jul 16. J Surg Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34270098
-
Transvaginal Natural Orifice Transluminal Endoscopic Nephrectomy in a Series of 63 Cases: Stepwise Transition From Hybrid to Pure NOTES.Eur Urol. 2015 Aug;68(2):302-10. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2015.03.033. Epub 2015 Mar 31. Eur Urol. 2015. PMID: 25837534
-
Transvaginal natural orifice specimen extraction surgery for 3D laparoscopic radical cystectomy: A cohort study.J Cancer Res Ther. 2023 Aug;19(4):892-897. doi: 10.4103/jcrt.jcrt_1612_22. J Cancer Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 37675713
-
Evaluation of the efficacy of natural orifice specimen extraction surgery versus conventional laparoscopic surgery for colorectal cancers: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Colorectal Dis. 2025 Jan;27(1):e17279. doi: 10.1111/codi.17279. Colorectal Dis. 2025. PMID: 39763245
-
Comparison of Major Clinical Outcomes Between Transvaginal NOTES and Traditional Laparoscopic Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.J Surg Res. 2019 Dec;244:278-290. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2019.06.012. Epub 2019 Jul 11. J Surg Res. 2019. PMID: 31302326
Cited by
-
Comparative evaluation of different specimen extraction techniques in laparoscopic simple nephrectomy in female patients.Int Urol Nephrol. 2025 Apr;57(4):1113-1121. doi: 10.1007/s11255-024-04294-0. Epub 2024 Nov 24. Int Urol Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 39580777
-
Cosmesis and feasibility of transvaginal natural orifice Specimen extraction (NOSE) for large organ specimen: a prospective pilot study.BMC Urol. 2022 Oct 29;22(1):165. doi: 10.1186/s12894-022-01114-4. BMC Urol. 2022. PMID: 36309743 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Transvaginal natural orifice specimen extraction surgery for left-sided colorectal resection: A single-centre cohort study.J Minim Access Surg. 2025 Jan 1;21(1):51-59. doi: 10.4103/jmas.jmas_108_24. Epub 2024 Dec 24. J Minim Access Surg. 2025. PMID: 39718944 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of natural duct specimen extraction versus conventional laparoscopic surgery for rectal cancer: a single-centre retrospective analysis.Am J Cancer Res. 2024 Sep 15;14(9):4472-4483. doi: 10.62347/XZHW4521. eCollection 2024. Am J Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39417176 Free PMC article.
-
Transvaginal natural orifice specimen extraction surgery in simple nephrectomy.Indian J Urol. 2025 Apr-Jun;41(2):104-110. doi: 10.4103/iju.iju_304_24. Epub 2025 Jan 29. Indian J Urol. 2025. PMID: 40292376 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

