Long noncoding RNA LINC00958 suppresses apoptosis and radiosensitivity of colorectal cancer through targeting miR-422a
- PMID: 34496838
- PMCID: PMC8425007
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-021-02188-0
Long noncoding RNA LINC00958 suppresses apoptosis and radiosensitivity of colorectal cancer through targeting miR-422a
Abstract
Background: Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) have been elucidated to participate in the development and progression of various cancers. In this study, we aimed to explore the underlying functions and mechanisms of LINC00958 in colorectal cancer.
Methods: LINC00958 expression in colorectal cancer tissues was examined by qRT-PCR. The correlations between LINC00958 expression and clinical characteristics and prognosis were evaluated. The biological functions of LINC00958 were detected by CCK-8, MTT, colony formation and flow cytometric analyses. RNA pulldown, RIP and luciferase reporter assays were used to confirm the regulatory effects of LINC00958 on miR-422a. Rescue experiments were performed to detect the effects of miR-422a on the roles of LINC00958.
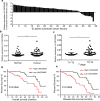
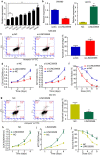
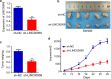
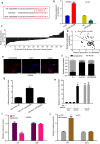
Results: LINC00958 was upregulated in colorectal cancer tissues and cell lines. High LINC00958 levels were positively associated with T stage and predicted poor prognosis. Cell experiments showed that LINC00958 promoted cell proliferation and suppressed apoptosis and sensitivity to radiotherapy in vitro and promoted tumor growth in vivo. Bioinformatics analysis predicted the binding site of miR-422a on LINC00958. Mechanistically, RNA pulldown, RIP and luciferase reporter assays demonstrated that LINC00958 specifically targeted miR-422a. In addition, we found that miR-422a suppressed MAPK1 expression by directly binding to the 3'-UTR of MAPK1, thereby inhibiting cell proliferation and enhancing cell apoptosis and radiosensitivity. Furthermore, miR-422a rescued the roles of LINC00958 in promoting MAPK1 expression and cell proliferation and decreasing cell apoptosis and radiosensitivity.
Conclusions: LINC00958 promoted MAPK1 expression and cell proliferation and suppressed cell apoptosis and radiosensitivity by targeting miR-422a, which suggests that it is a potential biomarker for the prognosis and treatment of colorectal cancer.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Colorectal cancer; LINC00958; Radiosensitivity; miR-422a.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors confirm that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
miR-422a inhibits cell proliferation in colorectal cancer by targeting AKT1 and MAPK1.Cancer Cell Int. 2017 Oct 28;17:91. doi: 10.1186/s12935-017-0461-3. eCollection 2017. Cancer Cell Int. 2017. PMID: 29118671 Free PMC article.
-
Long noncoding RNA LINC00958 promotes the oral squamous cell carcinoma by sponging miR-185-5p/YWHAZ.Life Sci. 2020 Feb 1;242:116782. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116782. Epub 2019 Aug 20. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 31442551
-
LINC00958 promotes bladder cancer carcinogenesis by targeting miR-490-3p and AURKA.BMC Cancer. 2021 Oct 26;21(1):1145. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08882-6. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34702201 Free PMC article.
-
Long Noncoding RNA CCDC26 Promotes Thyroid Cancer Malignant Progression via miR-422a/EZH2/Sirt6 Axis.Onco Targets Ther. 2021 May 11;14:3083-3094. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S282011. eCollection 2021. Onco Targets Ther. 2021. PMID: 34007185 Free PMC article.
-
Long Noncoding RNA LINC00958 Accelerates Gliomagenesis Through Regulating miR-203/CDK2.DNA Cell Biol. 2018 May;37(5):465-472. doi: 10.1089/dna.2018.4163. Epub 2018 Mar 23. DNA Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29570358
Cited by
-
Potential Role of MAP3K14 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Study Based on Comprehensive Bioinformatical Analysis and Validation.J Cancer. 2024 Mar 17;15(9):2731-2745. doi: 10.7150/jca.95322. eCollection 2024. J Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38577603 Free PMC article.
-
Construction, bioinformatics analysis, and validation of competitive endogenous RNA networks in ulcerative colitis.Front Genet. 2022 Aug 17;13:951243. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.951243. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36061211 Free PMC article.
-
Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Reveals Extensive Heterogeneity and Unique Gene Trajectories in Non-Transformed and Transformed Human Lung Epithelial Cells: Insights into the Role of LncRNAs in Tumor Heterogeneity.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 16;26(4):1690. doi: 10.3390/ijms26041690. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40004153 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNAs as biomarkers for predicting radioresistance and survival in cancer: a meta-analysis.Sci Rep. 2022 Nov 2;12(1):18494. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-21785-1. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36323697 Free PMC article.
-
The Mechanism of Long Non-coding RNA in Cancer Radioresistance/Radiosensitivity: A Systematic Review.Front Pharmacol. 2022 May 5;13:879704. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.879704. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35600868 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chen C, Liu WR, Zhang B, et al. LncRNA H19 downregulation confers erlotinib resistance through upregulation of PKM2 and phosphorylation of AKT in EGFR-mutant lung cancers. Cancer Lett. 2020;486(6):58–70. - PubMed
Grants and funding
- HWYX2019116/Henan Province 2019 overseas Research Project of Health Science and Technology Talents
- 201303132/Henan Medical Science and Technology Research Project
- No.201303163/Henan Medical Science and Technology Research Project
- 2018020432/Henan Medical Science and Technology Research Project
- CYQ20190073/Construction project of medical service capacity improvement project of medical institutions directly under Henan Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

