Ertugliflozin and Slope of Chronic eGFR: Prespecified Analyses from the Randomized VERTIS CV Trial
- PMID: 34497110
- PMCID: PMC8729577
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.01130121
Ertugliflozin and Slope of Chronic eGFR: Prespecified Analyses from the Randomized VERTIS CV Trial
Abstract
Background and objectives: A reduction in the rate of eGFR decline, with preservation of ≥0.75 ml/min per 1.73 m2 per year, has been proposed as a surrogate for kidney disease progression. We report results from prespecified analyses assessing effects of ertugliflozin versus placebo on eGFR slope from the eValuation of ERTugliflozin effIcacy and Safety CardioVascular outcomes (VERTIS CV) trial (NCT01986881).
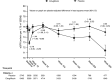
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: Patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease were randomized to placebo, ertugliflozin 5 mg, and ertugliflozin 15 mg (1:1:1). The analyses compared the effect of ertugliflozin (pooled doses, n=5499) versus placebo (n=2747) on eGFR slope per week and per year by random coefficient models. Study periods (weeks 0-6 and weeks 6-52) and total and chronic slopes (week 0 or week 6 to weeks 104, 156, 208, and 260) were modeled separately and by baseline kidney status.
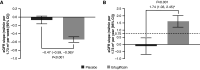
Results: In the overall population, for weeks 0-6, the least squares mean eGFR slopes (ml/min per 1.73 m2 per week [95% confidence interval (95% CI)]) were -0.07 (-0.16 to 0.03) and -0.54 (-0.61 to -0.48) for the placebo and ertugliflozin groups, respectively; the difference was -0.47 (-0.59 to -0.36). During weeks 6-52, least squares mean eGFR slopes (ml/min per 1.73 m2 per year [95% CI]) were -0.12 (-0.70 to 0.46) and 1.62 (1.21 to 2.02) for the placebo and ertugliflozin groups, respectively; the difference was 1.74 (1.03 to 2.45). For weeks 6-156, least squares mean eGFR slopes (ml/min per 1.73 m2 per year [95% CI]) were -1.51 (-1.70 to -1.32) and -0.32 (-0.45 to -0.19) for the placebo and ertugliflozin groups, respectively; the difference was 1.19 (0.95 to 1.42). During weeks 0-156, the placebo-adjusted difference in least squares mean slope was 1.06 (0.85 to 1.27). These findings were consistent by baseline kidney status.
Conclusions: Ertugliflozin has a favorable placebo-adjusted eGFR slope >0.75 ml/min per 1.73 m2 per year, documenting the kidney function preservation underlying the clinical benefits of ertugliflozin on kidney disease progression in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.
Clinical trial registry name and registration number: US National Library of Medicine, ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01986881. Date of trial registration: November 13, 2013.
Keywords: clinical trial; diabetic nephropathy; glomerular filtration rate; renal function decline; renal protection; sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Copyright © 2021 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures



Comment in
-
Are All SGLT2 Inhibitors Created Equal?Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2021 Sep;16(9):1309-1311. doi: 10.2215/CJN.09720721. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 34497107 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Perkovic V, Jardine MJ, Neal B, Bompoint S, Heerspink HJL, Charytan DM, Edwards R, Agarwal R, Bakris G, Bull S, Cannon CP, Capuano G, Chu PL, de Zeeuw D, Greene T, Levin A, Pollock C, Wheeler DC, Yavin Y, Zhang H, Zinman B, Meininger G, Brenner BM, Mahaffey KW; CREDENCE Trial Investigators: Canagliflozin and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med 380: 2295–2306, 2019 - PubMed
-
- Heerspink HJL, Stefánsson BV, Correa-Rotter R, Chertow GM, Greene T, Hou FF, Mann JFE, McMurray JJV, Lindberg M, Rossing P, Sjöström CD, Toto RD, Langkilde AM, Wheeler DC; DAPA-CKD Trial Committees and Investigators: Dapagliflozin in patients with chronic kidney disease. N Engl J Med 383: 1436–1446, 2020 - PubMed
-
- Cherney DZI, Heerspink HJL, Frederich R, Maldonado M, Liu J, Pong A, Xu ZJ, Patel S, Hickman A, Mancuso JP, Gantz I, Terra SG: Effects of ertugliflozin on renal function over 104 weeks of treatment: A post hoc analysis of two randomised controlled trials. Diabetologia 63: 1128–1140, 2020 - PMC - PubMed
-
- van Raalte DH, Cherney DZI: Sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibition and renal ischemia: Implications for future clinical trials. Kidney Int 94: 459–462, 2018 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

