Alternative treatments for type 2 diabetes and associated metabolic diseases: medical therapy or endoscopic duodenal mucosal remodelling?
- PMID: 34497147
- PMCID: PMC8515106
- DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-323931
Alternative treatments for type 2 diabetes and associated metabolic diseases: medical therapy or endoscopic duodenal mucosal remodelling?
Keywords: diabetes mellitus; duodenal mucosa; fatty liver; gastrointestinal endoscopy; glucose metabolism.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: MN is in the Scientific Advisory Board of Caelus Pharmaceuticals, The Netherlands, and Kaleido Biosciences, USA. None of these is directly relevant to the current paper. DH has received honoraria from Fractyl for participating in scientific advisory boards. There are no patents, products in development or marketed products to declare. The other authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

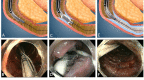
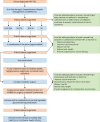
References
-
- NHS Digital . National diabetes audit programme, 2021. Available: https://digital.nhs.uk/data-and-information/clinical-audits-and-registri...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
