A lymphocyte-microglia-astrocyte axis in chronic active multiple sclerosis
- PMID: 34497421
- PMCID: PMC8719282
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-021-03892-7
A lymphocyte-microglia-astrocyte axis in chronic active multiple sclerosis
Abstract
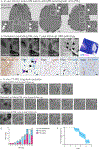
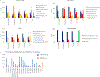
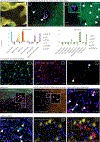
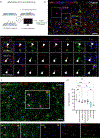
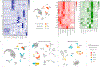
Multiple sclerosis (MS) lesions that do not resolve in the months after they form harbour ongoing demyelination and axon degeneration, and are identifiable in vivo by their paramagnetic rims on MRI scans1-3. Here, to define mechanisms underlying this disabling, progressive neurodegenerative state4-6 and foster development of new therapeutic agents, we used MRI-informed single-nucleus RNA sequencing to profile the edge of demyelinated white matter lesions at various stages of inflammation. We uncovered notable glial and immune cell diversity, especially at the chronically inflamed lesion edge. We define 'microglia inflamed in MS' (MIMS) and 'astrocytes inflamed in MS', glial phenotypes that demonstrate neurodegenerative programming. The MIMS transcriptional profile overlaps with that of microglia in other neurodegenerative diseases, suggesting that primary and secondary neurodegeneration share common mechanisms and could benefit from similar therapeutic approaches. We identify complement component 1q (C1q) as a critical mediator of MIMS activation, validated immunohistochemically in MS tissue, genetically by microglia-specific C1q ablation in mice with experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis, and therapeutically by treating chronic experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis with C1q blockade. C1q inhibition is a potential therapeutic avenue to address chronic white matter inflammation, which could be monitored by longitudinal assessment of its dynamic biomarker, paramagnetic rim lesions, using advanced MRI methods.
© 2021. This is a U.S. government work and not under copyright protection in the U.S.; foreign copyright protection may apply.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests. MA received consulting fees from Sanofi, unrelated to this study. PC received grant support from Annexon Biosciences for testing the anti-C1q-blocking antibody in EAE. The funders of the study had no role in the collection, analysis, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to submit the paper for publication.
Figures

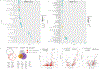



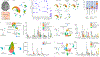


Comment in
-
Exploring new frontiers in multiple sclerosis.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2021 Nov;20(11):815. doi: 10.1038/d41573-021-00170-z. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2021. PMID: 34611330 No abstract available.
-
A lymphocyte-glia connection sets the pace for smoldering inflammation.Cell. 2021 Nov 11;184(23):5696-5698. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.10.018. Cell. 2021. PMID: 34767775
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

