Diabetes and pancreatic cancer: Exploring the two-way traffic
- PMID: 34497428
- PMCID: PMC8384733
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i30.4939
Diabetes and pancreatic cancer: Exploring the two-way traffic
Abstract
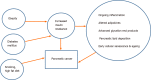
Pancreatic cancer (PC) is often associated with a poor prognosis. Long-standing diabetes mellitus is considered as an important risk factor for its development. This risk can be modified by the use of certain antidiabetic medications. On the other hand, new-onset diabetes can signal towards an underlying PC in the elderly population. Recently, several attempts have been made to develop an effective clinical tool for PC screening using a combination of history of new-onset diabetes and several other clinical and biochemical markers. On the contrary, diabetes affects the survival after treatment for PC. We describe this intimate and complex two-way relationship of diabetes and PC in this review by exploring the underlying pathogenesis.
Keywords: Chronic pancreatitis; Diabetes; New onset diabetes; Pancreatic adenocarcinoma; Pancreatic cancer; Type 3c diabetes.
©The Author(s) 2021. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors have no conflicts of interest to report.
Figures

References
-
- Mizrahi JD, Surana R, Valle JW, Shroff RT. Pancreatic cancer. Lancet. 2020;395:2008–2020. - PubMed
-
- IDF Diabetes Atlas 9th edition 2019. Sep 14, 2020. Available from: https://diabetesatlas.org/en/
-
- Kelly T, Yang W, Chen CS, Reynolds K, He J. Global burden of obesity in 2005 and projections to 2030. Int J Obes (Lond) 2008;32:1431–1437. - PubMed
-
- Rawla P, Thandra KC, Sunkara T. Pancreatic cancer and obesity: epidemiology, mechanism, and preventive strategies. Clin J Gastroenterol. 2019;12:285–291. - PubMed
-
- and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2014;37:S81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

