Clemastine Ameliorates Perioperative Neurocognitive Disorder in Aged Mice Caused by Anesthesia and Surgery
- PMID: 34497527
- PMCID: PMC8419266
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.738590
Clemastine Ameliorates Perioperative Neurocognitive Disorder in Aged Mice Caused by Anesthesia and Surgery
Abstract
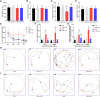
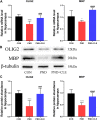
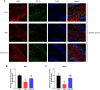
Perioperative neurocognitive disorder (PND) leads to progressive deterioration of cognitive function, especially in aged patients. Demyelination is closely associated with cognitive dysfunction. However, the relationship between PND and demyelination remains unclear. Here we showed that demyelination was related to the pathogenesis of PND. Clemastine, an antihistamine with potency in remyelination, was predicted to have a potential therapeutic effect on PND by next-generation sequencing and bioinformatics in our previous study. In the present study, it was given at 10 mg/kg per day for 2 weeks to evaluate the effects on PND in aged mice. We found that clemastine ameliorated PND and reduced the expression levels of inflammatory factors such as tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β). Further investigation suggested clemastine increased the expression of oligodendrocyte transcription factor 2 (OLIG2) and myelin basic protein (MBP) to enhance remyelination by inhibiting the overactivation of the WNT/β-catenin pathway. At the same time, the expression of post-synaptic density protein 95 (PSD95, or DLG4), brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), synaptosomal-associated protein 25 (SNAP25) and neuronal nuclei (NEUN) were also improved. Our results suggested that clemastine might be a therapy for PND caused by anesthetic and surgical factors in aged patients.
Keywords: clemastine; neuroinflammation; perioperative neurocognitive disorder; remyelination; synaptic plasticity; wnt/β-catenin signaling.
Copyright © 2021 Wu, Zhang, Zhou, Yang, Chen, Zhao, Zhong, Lin and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Transcranial near-infrared light promotes remyelination through AKT1/mTOR pathway to ameliorate postoperative neurocognitive disorder in aged mice.Neuroscience. 2025 Jan 26;565:358-368. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2024.12.007. Epub 2024 Dec 7. Neuroscience. 2025. PMID: 39653248
-
Surgery induces neurocognitive disorder via neuroinflammation and glymphatic dysfunction in middle-aged mice with brain lymphatic drainage impairment.Front Neurosci. 2024 Jun 20;18:1426718. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1426718. eCollection 2024. Front Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38975244 Free PMC article.
-
Transcranial near-infrared laser improves postoperative neurocognitive disorder in aged mice via SIRT3/AMPK/Nrf2 pathway.Front Neurosci. 2023 Jan 24;16:1100915. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.1100915. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36760797 Free PMC article.
-
Proposing Bromo-epi-androsterone (BEA) for perioperative neurocognitive disorders with Interleukin-6 as a druggable target.J Clin Anesth. 2025 Feb;101:111736. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2024.111736. Epub 2025 Jan 1. J Clin Anesth. 2025. PMID: 39746239 Review.
-
The Role of Perioperative Sleep Disturbance in Postoperative Neurocognitive Disorders.Nat Sci Sleep. 2021 Aug 6;13:1395-1410. doi: 10.2147/NSS.S320745. eCollection 2021. Nat Sci Sleep. 2021. PMID: 34393534 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cure of Alzheimer's Dementia Requires Addressing All of the Affected Brain Cell Types.J Clin Med. 2023 Mar 4;12(5):2049. doi: 10.3390/jcm12052049. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 36902833 Free PMC article.
-
General anesthetic agents induce neurotoxicity through oligodendrocytes in the developing brain.Zool Res. 2024 May 18;45(3):691-703. doi: 10.24272/j.issn.2095-8137.2023.413. Zool Res. 2024. PMID: 38766750 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clemastine and metformin extend the window of NMDA receptor surface expression in ageing oligodendrocyte precursor cells.Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 19;14(1):4091. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-53615-x. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38374232 Free PMC article.
-
Clemastine in remyelination and protection of neurons and skeletal muscle after spinal cord injury.Neural Regen Res. 2023 May;18(5):940-946. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.355749. Neural Regen Res. 2023. PMID: 36254972 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Discovery of Novel Drug Candidates for Alzheimer's Disease by Molecular Network Modeling.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Apr 15;14:850217. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.850217. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35493947 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

