GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: Beyond Their Pancreatic Effects
- PMID: 34497589
- PMCID: PMC8419463
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2021.721135
GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: Beyond Their Pancreatic Effects
Abstract
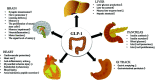
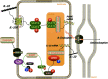
Glucagon like peptide-1 (GLP-1) is an incretin secretory molecule. GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) are widely used in the treatment of type 2 diabetes (T2DM) due to their attributes such as body weight loss, protection of islet β cells, promotion of islet β cell proliferation and minimal side effects. Studies have found that GLP-1R is widely distributed on pancreatic and other tissues and has multiple biological effects, such as reducing neuroinflammation, promoting nerve growth, improving heart function, suppressing appetite, delaying gastric emptying, regulating blood lipid metabolism and reducing fat deposition. Moreover, GLP-1RAs have neuroprotective, anti-infectious, cardiovascular protective, and metabolic regulatory effects, exhibiting good application prospects. Growing attention has been paid to the relationship between GLP-1RAs and tumorigenesis, development and prognosis in patient with T2DM. Here, we reviewed the therapeutic effects and possible mechanisms of action of GLP-1RAs in the nervous, cardiovascular, and endocrine systems and their correlation with metabolism, tumours and other diseases.
Keywords: GLP-1 receptor agonists; cancer; cardiovascular; endocrine; neurological.
Copyright © 2021 Zhao, Wang, Wen, Lu, Cui, Fu, Xue, Liu and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

