Cholecystokinin Expression in the Development of Myocardial Hypertrophy
- PMID: 34497680
- PMCID: PMC8405328
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/8231559
Cholecystokinin Expression in the Development of Myocardial Hypertrophy
Abstract
Background: Expression of cholecystokinin is found in myocardial tissues as a gastrointestinal hormone and may be involved in cardiovascular regulation. However, it is unclear whether there is an increase in cholecystokinin expression in myocardial hypertrophy progression induced by abdominal aortic constriction. The study is aimed at exploring the relationship between cholecystokinin expression and myocardial hypertrophy.
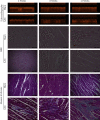
Methods: We randomly divided the 70 Sprague-Dawley rats into two groups: the sham operation group and the abdominal aortic constriction group. The hearts of rats were measured by echocardiography, and myocardial tissues and blood were collected at 4 weeks, 8 weeks, and 12 weeks after surgery. Morphological changes were assessed by microscopy. The cholecystokinin expression was evaluated by immunochemistry, Western blotting, quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
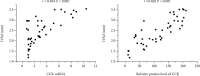
Results: The relative protein levels of cholecystokinin were significantly increased in the abdominal aortic constriction groups compared with the corresponding sham operation groups at 8 weeks and 12 weeks. The cholecystokinin mRNA in the abdominal aortic constriction groups was significantly higher than the time-matched sham operation groups. Changes in the left ventricular wall thickness were positively correlated with the relative protein levels of cholecystokinin and the mRNA of cholecystokinin.
Conclusions: The development of myocardial hypertrophy can affect the cholecystokinin expression of myocardial tissues.
Copyright © 2021 Zhongshu Han et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
