Artificial Intelligence Algorithm with ICD Coding Technology Guided by the Embedded Electronic Medical Record System in Medical Record Information Management
- PMID: 34497706
- PMCID: PMC8421187
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/3293457
Artificial Intelligence Algorithm with ICD Coding Technology Guided by the Embedded Electronic Medical Record System in Medical Record Information Management
Abstract
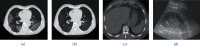
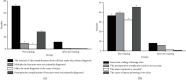
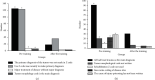
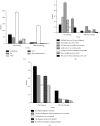
The study aims to explore the application of international classification of diseases (ICD) coding technology and embedded electronic medical record (EMR) system. The study established an EMR information knowledge system and collected the data of patient medical records and disease diagnostic codes on the front pages of 8 clinical departments of endocrinology, oncology, obstetrics and gynecology, ophthalmology, orthopedics, neurosurgery, and cardiovascular medicine for statistical analysis. Natural language processing-bidirectional recurrent neural network (NLP-BIRNN) algorithm was used to optimize medical records. The results showed that the coder was not clear about the basic rules of main diagnosis selection and the classification of disease coding and did not code according to the main diagnosis principles. The disease was not coded according to different conditions or specific classification, the code of postoperative complications was inaccurate, the disease diagnosis was incomplete, and the code selection was too general. The solutions adopted were as follows: communication and knowledge training should be strengthened for coders and medical personnel. BIRNN was compared with the convolutional neural network (CNN) and recurrent neural network (RNN) in accuracy, symptom accuracy, and symptom recall, and it suggested that the proposed BIRNN has higher value. Pathological language reading under artificial intelligence algorithm provides some convenience for disease diagnosis and treatment.
Copyright © 2021 Cheng Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Jia Z., Qin W., Duan H., Lv X., Li H. A hybrid method for ICD-10 auto-coding of Chinese diagnoses. Studies in Health Technology and Informatics. 2017;245(4):427–431. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

