Cannabidiol modulation of oxidative stress and signalling
- PMID: 34497718
- PMCID: PMC8385185
- DOI: 10.1042/NS20200080
Cannabidiol modulation of oxidative stress and signalling
Abstract
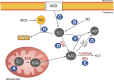
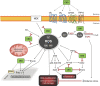
Cannabidiol (CBD), one of the primary non-euphoric components in the Cannabis sativa L. plant, has undergone clinical development over the last number of years as a therapeutic for patients with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome and Dravet syndromes. This phytocannabinoid demonstrates functional and pharmacological diversity, and research data indicate that CBD is a comparable antioxidant to common antioxidants. This review gathers the latest knowledge regarding the impact of CBD on oxidative signalling, with focus on the proclivity of CBD to regulate antioxidants and control the production of reactive oxygen species. CBD is considered an attractive therapeutic agent for neuroimmune disorders, and a body of literature indicates that CBD can regulate redox function at multiple levels, with a range of downstream effects on cells and tissues. However, pro-oxidant capacity of CBD has also been reported, and hence caution must be applied when considering CBD from a therapeutic standpoint. Such pro- and antioxidant functions of CBD may be cell- and model-dependent and may also be influenced by CBD dose, the duration of CBD treatment and the underlying pathology.
Keywords: Cannabidiol; Cannabinoids; Oxidative signalling; Oxidative stress; Reactive oxygen species.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

