Do Large Uterine Fibroids Impact Pregnancy Outcomes?
- PMID: 34497721
- PMCID: PMC8408619
- DOI: 10.5001/omj.2021.93
Do Large Uterine Fibroids Impact Pregnancy Outcomes?
Abstract
Objectives: We sought to assess the prevalence of fibroids complicating pregnancy among Omani women who delivered and were followed-up at Sultan Qaboos University Hospital (SQUH) and correlate the presence of large fibroids (> 5 cm) with maternal and neonatal outcomes.
Methods: This retrospective cohort study was conducted at the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, SQUH, from 1 January 2011 to 31 December 2016. Demographic data included maternal age, gravidity, parity, body mass index (BMI), and history of preterm delivery. Ultrasonographic data included the total number of fibroids, number of fibroids > 5 cm in diameter, and location. The main outcomes measured were preterm delivery, preterm premature rupture of membranes (PPROM), malpresentation, intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR), mode of delivery, postpartum hemorrhage, retained placenta, and cesarean myomectomy. Fetal outcomes included birth weight and Apgar score. We used the chi-square test and t-test to calculate significant outcomes.
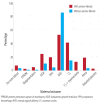
Results: The total number of deliveries over the study period was 24 800. Among these, 62 women had fibroids complicating pregnancy, giving an overall prevalence of 0.3%. Of the 62 women with documented uterine fibroids, 41 had fibroids > 5 cm in diameter and formed the study group, while the control group included 88 women with no fibroids and normal singleton pregnancies. The mean age, parity, BMI, and history of preterm delivery were comparable. The mean age of the study group was 32.6 years. There was no statistically significant difference in obstetric outcomes between the study and control group in terms of preterm labor (p =0.381), PPROM (p =0.536), malpresentation (p =0.237), IUGR (p =0.059), and retained placenta (p =0.296). Postpartum hemorrhage was significantly higher in the study group (p =0.018), the commonest cause was uterine atony (p =0.007). Women with large fibroids had a significantly increased cesarean section rate (p =0.002), the main indications were obstructed labor and failure to progress (62.5%). Five of the 44 women in the study group (12.8%) underwent cesarean myomectomy. Regarding neonatal outcomes, a statistically significant difference was noted in the Apgar scores.
Conclusions: Fibroids measuring > 5 cm in diameter are more likely to cause obstetric complications and are associated with higher cesarean rates. Pre-conception myomectomy is recommended for women with large fibroids.
Keywords: Cesarean Section; Postpartum Hemorrhage; Preterm Premature Rupture of the Membranes; Retrospective Studies.
The OMJ is Published Bimonthly and Copyrighted 2021 by the OMSB.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The influence of uterine fibroids on adverse outcomes in pregnant women: a meta-analysis.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2024 May 6;24(1):345. doi: 10.1186/s12884-024-06545-5. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2024. PMID: 38710995 Free PMC article.
-
Number and size of uterine fibroids and obstetric outcomes.J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2015 Mar;28(4):484-8. doi: 10.3109/14767058.2014.921675. Epub 2014 Jun 5. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2015. PMID: 24803127
-
Long-term obstetric, perinatal, and surgical complications in singleton pregnancies following previous cesarean myomectomy: a retrospective multicentric study.Front Surg. 2024 Aug 1;11:1430439. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2024.1430439. eCollection 2024. Front Surg. 2024. PMID: 39149134 Free PMC article.
-
Delivery for women with a previous cesarean: guidelines for clinical practice from the French College of Gynecologists and Obstetricians (CNGOF).Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2013 Sep;170(1):25-32. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2013.05.015. Epub 2013 Jun 28. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2013. PMID: 23810846 Review.
-
[Management of uterine myomas during pregnancy].Gynecol Obstet Fertil. 2016 Jun;44(6):350-4. doi: 10.1016/j.gyobfe.2016.04.007. Epub 2016 May 20. Gynecol Obstet Fertil. 2016. PMID: 27216952 Review. French.
Cited by
-
The characteristics of a fibroid in pregnancy can influence the perinatal outcome.Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2024 Oct;310(4):1905-1918. doi: 10.1007/s00404-024-07697-7. Epub 2024 Aug 29. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2024. PMID: 39207475
-
Arrest of labor secondary to large uterine fibroid.Clin Case Rep. 2024 Apr 20;12(4):e8806. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.8806. eCollection 2024 Apr. Clin Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 38645601 Free PMC article.
-
High-risk factors for massive haemorrhage in medical abortion patients with missed miscarriage.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2024 Sep 9;24(1):521. doi: 10.1186/s12884-024-06682-x. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2024. PMID: 39245736 Free PMC article.
-
Management of Unintended Pregnancy, Complicated by the Presence of Intrauterine Contraceptive Device and a Large Uterine Fibroid: A Case Report.Cureus. 2025 Feb 22;17(2):e79466. doi: 10.7759/cureus.79466. eCollection 2025 Feb. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40130152 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of the Clinical Presentations and Ultrasonographic Features of Uterine Fibroids in Adult Africans: A Retrospective Study.Oman Med J. 2023 Jan 31;38(1):e459. doi: 10.5001/omj.2023.36. eCollection 2023 Jan. Oman Med J. 2023. PMID: 36908828 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sampat K, Alleemudder DI. Fibroid in pregnancy: management and outcome. TOG 2018;20(3):187-195 .10.1111/tog.12491 - DOI
-
- Mitra D, Bhatti S, Iskaros JP. 86 outcome of pregnancies with uterine leiomyoma: a population based retrospective study. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 2013;98(Suppl 1):A104-A105 .10.1136/archdischild-2013-303966.361 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources