The role of deep eutectic solvents and carrageenan in synthesizing biocompatible anisotropic metal nanoparticles
- PMID: 34497740
- PMCID: PMC8381852
- DOI: 10.3762/bjnano.12.69
The role of deep eutectic solvents and carrageenan in synthesizing biocompatible anisotropic metal nanoparticles
Abstract
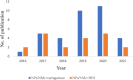
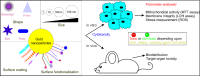
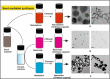
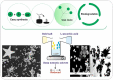
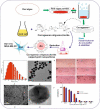
Plasmonic metal nanoparticles are widely used for many applications due to their unique optical and chemical properties. Over the past decade, anisotropic metal nanoparticles have been explored for imaging, sensing, and diagnostic applications. The variations and flexibility of tuning the size and shape of the metal nanoparticles at the nanoscale made them promising candidates for biomedical applications such as therapeutics, diagnostics, and drug delivery. However, safety and risk assessment of the nanomaterials for clinical purposes are yet to be made owing to their cytotoxicity. The toxicity concern is primarily due to the conventional synthesis route that involves surfactants as a structure-directing agent and as a capping agent for nanoparticles. Wet chemical methods employ toxic auxiliary chemicals. However, the approach yields monodispersed nanoparticles, an essential criterion for their intended application and a limitation of the green synthesis of nanoparticles using plant extracts. Several biocompatible counterparts such as polymers, lipids, and chitosan-based nanoparticles have been successfully used in the synthesis of safe nanomaterials, but there were issues regarding reproducibility and yield. Enzymatic degradation was one of the factors responsible for limiting the efficacy. Hence, it is necessary to develop a safer and nontoxic route towards synthesizing biocompatible nanomaterials while retaining morphology, high yield, and monodispersity. In this regard, deep eutectic solvents (DESs) and carrageenan as capping agent for nanoparticles can ensure the safety. Carrageenan has the potential to act as antibacterial and antiviral agent, and adds enhanced stability to the nanoparticles. This leads to a multidimensional approach for utilizing safe nanomaterials for advanced biomedical and clinical applications.
Keywords: anisotropic nanoparticles; carrageenan; cytotoxicity; eutectic solvents; surfactants.
Copyright © 2021, Das et al.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
