Impact of Smoking History on Response to Immunotherapy in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 34497760
- PMCID: PMC8419340
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.703143
Impact of Smoking History on Response to Immunotherapy in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Objectives: To evaluate the impact of smoking history on the clinical benefit of immunotherapy in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Methods: Twenty-three randomized clinical trials and seven real-world studies were included in this meta-analysis. Hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) and odds ratios for the overall response rate (ORR) were extracted. A fixed-effects or random-effects model was applied to obtain pooled estimates.
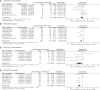
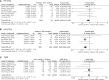
Results: Data from 16 high-quality trials involving 10,643 NSCLC patients receiving either immunotherapy or chemotherapy/placebo enabled direct comparison of the survival impact of smoking. Anti-PD-1/PD-L1/CTLA-4 immunotherapy was found to significantly prolong OS and PFS as compared to chemotherapy/placebo in smokers (HR for OS, 0.76 [0.69-0.83], P<0.00001; HR for PFS, 0.65 [0.56-0.75], P<0.00001), and these trends were less or not significant in non-smokers (HR for OS, 0.91 [0.78-1.06], P=0.25; HR for PFS, 0.68 [0.45-1.03], P=0.07). Consistent results were obtained for the first-line or second/third-line use of immunotherapy and for non-squamous NSCLC patients only. Furthermore, the data from 7 trials and 7 real-world studies involving 4,777 patients receiving immunotherapy allowed direct comparison of therapeutic outcomes between smokers and non-smokers. Prolonged OS (HR 0.86 [0.75-0.99], P=0.04) and PFS (HR 0.69 [0.60-0.81], P<0.0001) and a higher response rate (ORR 1.20 [0.94-1.53], P=0.15) were observed in smokers compared to non-smokers receiving immunotherapy.
Conclusions: Immunotherapy was found to have a greater benefit in NSCLC patients with a smoking history than in those who had never smoked.
Keywords: clinical benefit; immunotherapy; meta-analysis; non-small cell lung cancer; smoking.
Copyright © 2021 Zhao, Jiang, Wang, He, Su and Yu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

