From Immunogenic Cell Death to Immunogenic Modulation: Select Chemotherapy Regimens Induce a Spectrum of Immune-Enhancing Activities in the Tumor Microenvironment
- PMID: 34497771
- PMCID: PMC8419351
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.728018
From Immunogenic Cell Death to Immunogenic Modulation: Select Chemotherapy Regimens Induce a Spectrum of Immune-Enhancing Activities in the Tumor Microenvironment
Abstract
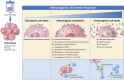
Cancer treatment has rapidly entered the age of immunotherapy, and it is becoming clear that the effective therapy of established tumors necessitates rational multi-combination immunotherapy strategies. But even in the advent of immunotherapy, the clinical role of standard-of-care chemotherapy regimens still remains significant and may be complementary to emerging immunotherapeutic approaches. Depending on dose, schedule, and agent, chemotherapy can induce immunogenic cell death, resulting in the release of tumor antigens to stimulate an immune response, or immunogenic modulation, sensitizing surviving tumor cells to immune cell killing. While these have been previously defined as distinct processes, in this review we examine the published mechanisms supporting both immunogenic cell death and immunogenic modulation and propose they be reclassified as similar effects termed "immunogenic cell stress." Treatment-induced immunogenic cell stress is an important result of cytotoxic chemotherapy and future research should consider immunogenic cell stress as a whole rather than just immunogenic cell death or immunogenic modulation. Cancer treatment strategies should be designed specifically to take advantage of these effects in combination immunotherapy, and novel chemotherapy regimens should be designed and investigated to potentially induce all aspects of immunogenic cell stress.
Keywords: cancer; cell stress; chemotherapy; immunogenic cell death; immunogenic modulation; immunotherapy.
Copyright © 2021 Fabian, Wolfson and Hodge.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Shields M. Chapter 14 - Chemotherapeutics. In: Badal Mccreath S, Delgoda R, editors. Pharmacognosy: Fundamentals, Applications and Strategies. Boston: Academic Press; (2016). p. 295–313.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

