Right Ventricular Function Predicts Adverse Clinical Outcomes in Patients With Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension: A Three-Dimensional Echocardiographic Study
- PMID: 34497813
- PMCID: PMC8419302
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2021.697396
Right Ventricular Function Predicts Adverse Clinical Outcomes in Patients With Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension: A Three-Dimensional Echocardiographic Study
Abstract
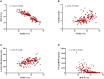
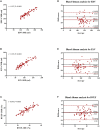
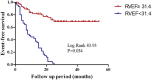
Background: Right ventricular (RV) function plays a vital role in the prognosis of patients with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH). We used new machine learning (ML)-based fully automated software to quantify RV function using three-dimensional echocardiography (3DE) to predict adverse clinical outcomes in CTEPH patients. Methods: A total of 151 consecutive CTEPH patients were registered in this prospective study between April 2015 and July 2019. New ML-based methods were used for data management, and quantitative analysis of RV volume and ejection fraction (RVEF) was performed offline. RV structural and functional parameters were recorded using 3DE. CTEPH was diagnosed using right heart catheterization, and 62 patients underwent cardiac magnetic resonance to assess right heart function. Adverse clinical outcomes were defined as PH-related hospitalization with hemoptysis or increased RV failure, including conditions requiring balloon pulmonary angioplasty or pulmonary endarterectomy, as well as death. Results: The median follow-up time was 19.7 months (interquartile range, 0.5-54 months). Among the 151 CTEPH patients, 72 experienced adverse clinical outcomes. Multivariate Cox proportional-hazard analysis showed that ML-based 3DE analysis of RVEF was a predictor of adverse clinical outcomes (hazard ratio, 1.576; 95% confidence interval (CI), 1.046~2.372; P = 0.030). Conclusions: The new ML-based 3DE algorithm is a promising technique for rapid 3D quantification of RV function in CTEPH patients.
Keywords: clinical failure; machine learning; prognosis; pulmonary hypertension; right ventricular function; three-dimensional echocardiography.
Copyright © 2021 Li, Liang, Guo, Yang, Gong, Zhang, Zhang, Jiang and Lu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Ende-Verhaar YM, Cannegieter SC, Vonk Noordegraaf A, Delcroix M, Pruszczyk P, Mairuhu AT, et al. Incidence of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension after acute pulmonary embolism: a contemporary view of the published literature. Eur Respir J. (2017) 49:1601792. 10.1183/13993003.01792-2016 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

