The versatility of plant organic acid metabolism in leaves is underpinned by mitochondrial malate-citrate exchange
- PMID: 34498076
- PMCID: PMC8643697
- DOI: 10.1093/plcell/koab223
The versatility of plant organic acid metabolism in leaves is underpinned by mitochondrial malate-citrate exchange
Abstract
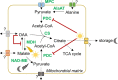
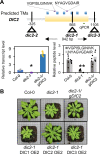
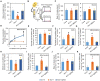
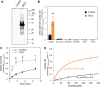
Malate and citrate underpin the characteristic flexibility of central plant metabolism by linking mitochondrial respiratory metabolism with cytosolic biosynthetic pathways. However, the identity of mitochondrial carrier proteins that influence both processes has remained elusive. Here we show by a systems approach that DICARBOXYLATE CARRIER 2 (DIC2) facilitates mitochondrial malate-citrate exchange in vivo in Arabidopsis thaliana. DIC2 knockout (dic2-1) retards growth of vegetative tissues. In vitro and in organello analyses demonstrate that DIC2 preferentially imports malate against citrate export, which is consistent with altered malate and citrate utilization in response to prolonged darkness of dic2-1 plants or a sudden shift to darkness of dic2-1 leaves. Furthermore, isotopic glucose tracing reveals a reduced flux towards citrate in dic2-1, which results in a metabolic diversion towards amino acid synthesis. These observations reveal the physiological function of DIC2 in mediating the flow of malate and citrate between the mitochondrial matrix and other cell compartments.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of American Society of Plant Biologists.
Figures




References
-
- Araújo WL, Tohge T, Nunes-Nesi A, Obata T, Fernie AR (2014) Analysis of kinetic labeling of amino acids and organic acids by GC-MS. InDieuaide-Noubhani M, Alonso AP, eds, Plant Metabolic Flux Analysis: Methods and Protocols. Humana Press, Totowa, NJ, pp 107–119 - PubMed
-
- Ashykhmina N, Lorenz M, Frerigmann H, Koprivova A, Hofsetz E, Stührwohldt N, Flügge U-I, Haferkamp I, Kopriva S, Gigolashvili T (2019) PAPST2 plays critical roles in removing the stress signaling molecule 3′-phosphoadenosine 5′-phosphate from the cytosol and its subsequent degradation in plastids and mitochondria. Plant Cell 31: 231–249 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baud S, Guyon V, Kronenberger J, Wuillème S, Miquel M, Caboche M, Lepiniec L, Rochat C (2003) Multifunctional acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1 is essential for very long chain fatty acid elongation and embryo development in Arabidopsis. Plant J 33: 75–86 - PubMed
-
- Bernard SM, Habash DZ (2009) The importance of cytosolic glutamine synthetase in nitrogen assimilation and recycling. New Phytol 182: 608–620 - PubMed
-
- Bykova NV, Møller IM, Gardeström P, Igamberdiev AU (2014) The function of glycine decarboxylase complex is optimized to maintain high photorespiratory flux via buffering of its reaction products. Mitochondrion 19: 357–364 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

