Cycling in a crowd: Coordination of plant cell division, growth, and cell fate
- PMID: 34498091
- PMCID: PMC8774096
- DOI: 10.1093/plcell/koab222
Cycling in a crowd: Coordination of plant cell division, growth, and cell fate
Abstract
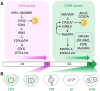
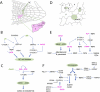
The reiterative organogenesis that drives plant growth relies on the constant production of new cells, which remain encased by interconnected cell walls. For these reasons, plant morphogenesis strictly depends on the rate and orientation of both cell division and cell growth. Important progress has been made in recent years in understanding how cell cycle progression and the orientation of cell divisions are coordinated with cell and organ growth and with the acquisition of specialized cell fates. We review basic concepts and players in plant cell cycle and division, and then focus on their links to growth-related cues, such as metabolic state, cell size, cell geometry, and cell mechanics, and on how cell cycle progression and cell division are linked to specific cell fates. The retinoblastoma pathway has emerged as a major player in the coordination of the cell cycle with both growth and cell identity, while microtubule dynamics are central in the coordination of oriented cell divisions. Future challenges include clarifying feedbacks between growth and cell cycle progression, revealing the molecular basis of cell division orientation in response to mechanical and chemical signals, and probing the links between cell fate changes and chromatin dynamics during the cell cycle.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of American Society of Plant Biologists.
Figures


Comment in
-
Back to the roots: A focus on plant cell biology.Plant Cell. 2022 Jan 20;34(1):1-3. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koab278. Plant Cell. 2022. PMID: 34755878 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Ahmad Z, Magyar Z, Bögre L, Papdi C (2019) Cell cycle control by the target of rapamycin signalling pathway in plants. J Exp Bot 70: 2275–2284 - PubMed
-
- Asada T (2019) Preprophase-band positioning in isolated tobacco BY-2 cells: evidence for a principal role of nucleus-cell cortex interaction in default division-plane selection. Protoplasma 256: 721–729 - PubMed
-
- Barrada A, Djendli M, Desnos T, Mercier R, Robaglia C, Montané M-H, Menand B (2019) A TOR-YAK1 signaling axis controls cell cycle, meristem activity and plant growth in Arabidopsis. Development 146: dev171298 - PubMed

