Defects in the STIM1 SOARα2 domain affect multiple steps in the CRAC channel activation cascade
- PMID: 34498097
- PMCID: PMC8558294
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-021-03933-4
Defects in the STIM1 SOARα2 domain affect multiple steps in the CRAC channel activation cascade
Abstract
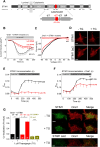
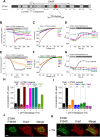
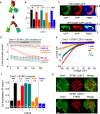
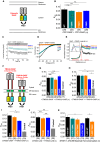
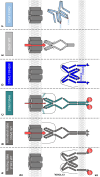
The calcium release-activated calcium (CRAC) channel consists of STIM1, a Ca2+ sensor in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), and Orai1, the Ca2+ ion channel in the plasma membrane. Ca2+ store depletion triggers conformational changes and oligomerization of STIM1 proteins and their direct interaction with Orai1. Structural alterations include the transition of STIM1 C-terminus from a folded to an extended conformation thereby exposing CAD (CRAC activation domain)/SOAR (STIM1-Orai1 activation region) for coupling to Orai1. In this study, we discovered that different point mutations of F394 in the small alpha helical segment (STIM1 α2) within the CAD/SOAR apex entail a rich plethora of effects on diverse STIM1 activation steps. An alanine substitution (STIM1 F394A) destabilized the STIM1 quiescent state, as evident from its constitutive activity. Single point mutation to hydrophilic, charged amino acids (STIM1 F394D, STIM1 F394K) impaired STIM1 homomerization and subsequent Orai1 activation. MD simulations suggest that their loss of homomerization may arise from altered formation of the CC1α1-SOAR/CAD interface and potential electrostatic interactions with lipid headgroups in the ER membrane. Consistent with these findings, we provide experimental evidence that the perturbing effects of F394D depend on the distance of the apex from the ER membrane. Taken together, our results suggest that the CAD/SOAR apex is in the immediate vicinity of the ER membrane in the STIM1 quiescent state and that different mutations therein can impact the STIM1/Orai1 activation cascade in various manners. Legend: Upon intracellular Ca2+ store depletion of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), Ca2+ dissociates from STIM1. As a result, STIM1 adopts an elongated conformation and elicits Ca2+ influx from the extracellular matrix (EM) into the cell due to binding to and activation of Ca2+-selective Orai1 channels (left). The effects of three point mutations within the SOARα2 domain highlight the manifold roles of this region in the STIM1/Orai1 activation cascade: STIM1 F394A is active irrespective of the intracellular ER Ca2+ store level, but activates Orai1 channels to a reduced extent (middle). On the other hand, STIM1 F394D/K cannot adopt an elongated conformation upon Ca2+ store-depletion due to altered formation of the CC1α1-SOAR/CAD interface and/or electrostatic interaction of the respective side-chain charge with corresponding opposite charges on lipid headgroups in the ER membrane (right).
Keywords: CAD; CRAC channels; Molecular dynamics; OASF; Orai1; Protein-membrane interaction; SOAR; STIM1.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Modulation of Orai1 and STIM1 by Cellular Factors.In: Kozak JA, Putney JW Jr, editors. Calcium Entry Channels in Non-Excitable Cells. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2018. Chapter 4. In: Kozak JA, Putney JW Jr, editors. Calcium Entry Channels in Non-Excitable Cells. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2018. Chapter 4. PMID: 30299655 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
A novel STIM1-Orai1 gating interface essential for CRAC channel activation.Cell Calcium. 2019 May;79:57-67. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2019.02.009. Epub 2019 Feb 23. Cell Calcium. 2019. PMID: 30831274
-
A Cytosolic Homomerization and a Modulatory Domain within STIM1 C Terminus Determine Coupling to ORAI1 Channels.J Biol Chem. 2009 Mar 27;284(13):8421-6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C800229200. Epub 2009 Feb 3. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19189966 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping interactions between the CRAC activation domain and CC1 regulating the activity of the ER Ca2+ sensor STIM1.J Biol Chem. 2022 Aug;298(8):102157. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102157. Epub 2022 Jun 17. J Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 35724962 Free PMC article.
-
Optogenetic Approaches to Control Calcium Entry in Non-Excitable Cells.In: Kozak JA, Putney JW Jr, editors. Calcium Entry Channels in Non-Excitable Cells. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2018. Chapter 8. In: Kozak JA, Putney JW Jr, editors. Calcium Entry Channels in Non-Excitable Cells. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2018. Chapter 8. PMID: 30299659 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
CRAC and SK Channels: Their Molecular Mechanisms Associated with Cancer Cell Development.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Dec 23;15(1):101. doi: 10.3390/cancers15010101. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36612099 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The many states of STIM1.Elife. 2021 Dec 7;10:e75174. doi: 10.7554/eLife.75174. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34875211 Free PMC article.
-
STIM1 functions as a proton sensor to coordinate cytosolic pH with store-operated calcium entry.J Biol Chem. 2024 Dec;300(12):107924. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107924. Epub 2024 Oct 23. J Biol Chem. 2024. PMID: 39454952 Free PMC article.
-
Injectable, Adhesive, and Self-Healing Composite Hydrogels Loaded With Oxybutynin Hydrochloride for the Treatment of Overactive Bladder in Rats.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Jun 27;10:906835. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.906835. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35832402 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Lipids in CRAC Channel Function.Biomolecules. 2022 Feb 23;12(3):352. doi: 10.3390/biom12030352. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35327543 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Roos J, DiGregorio PJ, Yeromin AV, Ohlsen K, Lioudyno M, Zhang S, Safrina O, Kozak JA, Wagner SL, Cahalan MD, Velicelebi G, Stauderman KA. STIM1, an essential and conserved component of store-operated Ca2+ channel function. J Cell Biol. 2005;169(3):435–445. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200502019. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhang SL, Yeromin AV, Zhang XHF, Yu Y, Safrina O, Penna A, Roos J, Stauderman KA, Cahalan MD. Genome-wide RNAi screen of Ca2+ influx identifies genes that regulate Ca2+ release-activated Ca2+ channel activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2006;103(24):9357–9362. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0603161103. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

