A novel intronic circular RNA, circGNG7, inhibits head and neck squamous cell carcinoma progression by blocking the phosphorylation of heat shock protein 27 at Ser78 and Ser82
- PMID: 34498800
- PMCID: PMC8626595
- DOI: 10.1002/cac2.12213
A novel intronic circular RNA, circGNG7, inhibits head and neck squamous cell carcinoma progression by blocking the phosphorylation of heat shock protein 27 at Ser78 and Ser82
Abstract
Background: There is increasing evidence that circular RNAs (circRNAs) play a significant role in pathological processes including tumorigenesis. In contrast to exonic circRNAs, which are the most frequently reported circRNAs in cancer so far, the studies of intronic circRNAs have been greatly lagged behind. Here, we aimed to investigate the regulatory role of intronic circRNAs in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC).
Methods: We conducted whole-transcriptome sequencing with four pairs of primary tumor tissues and adjacent normal tissues from HNSCC patients. Then, we characterized circGNG7 expression in HNSCC tissues and cell lines and explored its association with the prognosis of HNSCC patients. We also identified interactions between circGNG7 and functional proteins, which alter downstream signaling that regulate HNSCC progression.
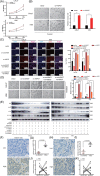
Results: In this study, we identified a new intronic circRNA, circGNG7, and validated its functional roles in HNSCC progression. CircGNG7 was predominately localized to the cytoplasm, and its expression was downregulated in both HNSCC tissues andCAL27, CAL33, SCC4, SCC9, HN6, and HN30 cells. Low expression of circGNG7 was significantly correlated with poor prognosis in HNSCC patients. Consistent with this finding, overexpression of circGNG7 strongly inhibited tumor cell proliferation, colony formation, in vitro migration, and in vivo tumor growth. Mechanistically, the expression of circGNG7 in HNSCC cells was regulated by the transcription factor SMAD family member 4 (SMAD4). Importantly, we discovered that circGNG7 could bind to serine residues 78 and 82 of the functional heat shock protein 27 (HSP27), occupying its phosphorylation sites and hindering its phosphorylation, which reduced HSP27-JNK/P38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) oncogenic signaling. Downregulation of circGNG7 expression in HNSCC increased HSP27-JNK/P38 MAPK signaling and promoted tumor progression.
Conclusions: Our results revealed that a new intronic circRNA, circGNG7, functions as a strong tumor suppressor and that circGNG7/HSP27-JNK/P38 MAPK signaling is a novel mechanism by which HNSCC progression can be controlled.
Keywords: circGNG7; head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; heat shock protein 27 (HSP27); intronic circular RNAs; mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling; phosphorylation; tumor suppressor.
© 2021 The Authors. Cancer Communications published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd. on behalf of Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


 ) and convergent primers (
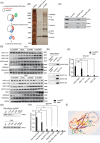
) and convergent primers ( ) in CAL27 cells. GAPDH was used as a linear RNA control. The head‐to‐tail splicing of circGNG7 was confirmed by Sanger sequencing in CAL27 cells. (C) RNA samples were treated with RNase R to remove linear RNAs, and circGNG7 was evaluated after RNase R digestion in CAL27 and HN6 cells. For qPCR normalization, the abundance of GNG7 was calculated by standardizing over the spike DNA control and setting the PBS control. (D) RT‐PCR for the abundance of circGNG7 and GNG7 in CAL27 and HN6 cells treated with actinomycin D at the indicated time points. Data are presented as mean ± SD of at least three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. Abbreviations: HNSCC: head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; qPCR: quantitative real‐time polymerase chain reaction; RT‐PCR: reverse transcription PCR; GNG7: G protein subunit gamma 7; cDNA: complementary DNA; gDNA: genomic DNA
) in CAL27 cells. GAPDH was used as a linear RNA control. The head‐to‐tail splicing of circGNG7 was confirmed by Sanger sequencing in CAL27 cells. (C) RNA samples were treated with RNase R to remove linear RNAs, and circGNG7 was evaluated after RNase R digestion in CAL27 and HN6 cells. For qPCR normalization, the abundance of GNG7 was calculated by standardizing over the spike DNA control and setting the PBS control. (D) RT‐PCR for the abundance of circGNG7 and GNG7 in CAL27 and HN6 cells treated with actinomycin D at the indicated time points. Data are presented as mean ± SD of at least three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. Abbreviations: HNSCC: head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; qPCR: quantitative real‐time polymerase chain reaction; RT‐PCR: reverse transcription PCR; GNG7: G protein subunit gamma 7; cDNA: complementary DNA; gDNA: genomic DNA


References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 2019; 69: 7‐34. - PubMed
-
- Lau A, Yang WF, Li KY, Su YX. Systemic therapy in recurrent or metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma‐ a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2020; 153: 102984. - PubMed
-
- Marur S, Forastiere AA. Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: update on epidemiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Mayo Clin Proc. 2016; 91: 386‐396. - PubMed
-
- Li J, Sun D, Pu W, Wang J, Peng Y. Circular RNAs in cancer: biogenesis, function, and clinical significance. Trends Cancer. 2020; 6: 319‐336. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

