Low-Cost Synthesis of Silicon Quantum Dots with Near-Unity Internal Quantum Efficiency
- PMID: 34498875
- PMCID: PMC8474143
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.1c02187
Low-Cost Synthesis of Silicon Quantum Dots with Near-Unity Internal Quantum Efficiency
Abstract
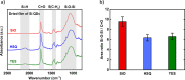
As a cost-effective batch synthesis method, Si quantum dots (QDs) with near-infrared photoluminescence, high quantum yield (>50% in polymer nanocomposite), and near-unity internal quantum efficiency were fabricated from an inexpensive commercial precursor (triethoxysilane, TES), using optimized annealing and etching processes. The optical properties of such QDs are similar to those prepared from state-of-the-art precursors (hydrogen silsesquioxane, HSQ) yet featuring an order of magnitude lower cost. To understand the effect of synthesis parameters on QD optical properties, we conducted a thorough comparison study between common solid precursors: TES, HSQ, and silicon monoxide (SiO), including chemical, structural, and optical characterizations. We found that the structural nonuniformity and abundance of oxide inherent to SiO limited the resultant QD performance, while for TES-derived QDs this drawback can be avoided. The presented low-cost synthetic approach would significantly favor applications requiring high loading of good-quality Si QDs, such as light conversion for photovoltaics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

References
-
- Henderson E. J.; Shuhendler A. J.; Prasad P.; Baumann V.; Maier-Flaig F.; Faulkner D. O.; Lemmer U.; Wu X. Y.; Ozin G. A. Colloidally Stable Silicon Nanocrystals with Near-Infrared Photoluminescence for Biological Fluorescence Imaging. Small 2011, 7, 2507–2516. 10.1002/smll.201100845. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

