Correlation between kidney sodium and potassium handling and the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in children with hypertensive disorders
- PMID: 34499251
- PMCID: PMC8904647
- DOI: 10.1007/s00467-021-05204-7
Correlation between kidney sodium and potassium handling and the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in children with hypertensive disorders
Abstract
Background: Urine sodium and potassium are used as surrogate markers for dietary consumption in adults with hypertension, but their role in youth with hypertension and their association with components of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) are incompletely characterized. Some individuals with hypertension may have an abnormal RAAS response to dietary sodium and potassium intake, though this is incompletely described. Our objective was to investigate if plasma renin activity and serum aldosterone are associated with urine sodium and potassium in youth referred for hypertensive disorders.
Methods: This pilot study was a cross-sectional analysis of baseline data from 44 youth evaluated for hypertensive disorders in a Hypertension Clinic. We recorded urine sodium and potassium concentrations normalized to urine creatinine, plasma renin activity, and serum aldosterone and calculated the sodium/potassium (UNaK) and aldosterone/renin ratios. We used multivariable generalized linear models to estimate the associations of renin and aldosterone with urine sodium and potassium.
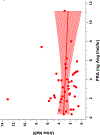
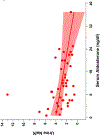
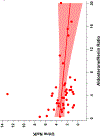
Results: Our cohort was diverse (37% non-Hispanic Black, 14% Hispanic), 66% were male, and median age was 15.3 years; 77% had obesity and 9% had a secondary etiology. Aldosterone was associated inversely with urine sodium/creatinine (β: -0.34, 95% CI -0.62 to -0.06) and UNaK (β: -0.09, 95% CI -0.16 to -0.03), and adjusted for estimated glomerular filtration rate and serum potassium.
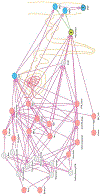
Conclusions: Higher serum aldosterone levels, but not plasma renin activity, were associated with lower urine sodium/creatinine and UNaK at baseline in youth referred for hypertensive disorders. Further characterization of the RAAS could help define hypertension phenotypes and guide management. A higher resolution version of the Graphical abstract is available as supplementary information.
Keywords: Biomarker; Blood pressure; Directed acyclic graph; Natriuresis; Pediatric; UNaK; Youth.
© 2021. IPNA.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Renal BOLD-MRI relates to kidney function and activity of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in hypertensive patients.J Hypertens. 2015 Mar;33(3):597-603; discussion 603-4. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000000436. J Hypertens. 2015. PMID: 25479032
-
Chronobiology of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in dogs: relation to blood pressure and renal physiology.Chronobiol Int. 2013 Nov;30(9):1144-59. doi: 10.3109/07420528.2013.807275. Epub 2013 Aug 9. Chronobiol Int. 2013. PMID: 23931032
-
An evaluation of renin-angiotensin system markers in youth with type 2 diabetes and associations with renal outcomes.Pediatr Diabetes. 2020 Nov;21(7):1102-1109. doi: 10.1111/pedi.13081. Epub 2020 Aug 25. Pediatr Diabetes. 2020. PMID: 32657529
-
K+ and the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system: new insights into their role in blood pressure control and hypertension treatment.J Physiol. 2019 Sep;597(17):4451-4464. doi: 10.1113/JP276844. Epub 2019 Jul 29. J Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31294465 Review.
-
Impact of Salt Intake on the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Hypertension.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;956:61-84. doi: 10.1007/5584_2016_147. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 27757935 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of sodium intake, age, gender, blood sampling time on distribution of plasma aldosterone, renin activity, deoxycorticosterone, cortisol, cortisone, and 24 h urinary aldosterone levels in normotensive individuals based on LC-MS/MS.Endocrine. 2024 Aug;85(2):947-954. doi: 10.1007/s12020-024-03899-w. Epub 2024 Jun 4. Endocrine. 2024. PMID: 38833202
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

