Molecular mechanisms underlying the role of the centriolar CEP164-TTBK2 complex in ciliopathies
- PMID: 34499853
- PMCID: PMC8752127
- DOI: 10.1016/j.str.2021.08.007
Molecular mechanisms underlying the role of the centriolar CEP164-TTBK2 complex in ciliopathies
Abstract
Cilia formation is essential for human life. One of the earliest events in the ciliogenesis program is the recruitment of tau-tubulin kinase 2 (TTBK2) by the centriole distal appendage component CEP164. Due to the lack of high-resolution structural information on this complex, it is unclear how it is affected in human ciliopathies such as nephronophthisis. Furthermore, it is poorly understood if binding to CEP164 influences TTBK2 activities. Here, we present a detailed biochemical, structural, and functional analysis of the CEP164-TTBK2 complex and demonstrate how it is compromised by two ciliopathic mutations in CEP164. Moreover, we also provide insights into how binding to CEP164 is coordinated with TTBK2 activities. Together, our data deepen our understanding of a crucial step in cilia formation and will inform future studies aimed at restoring CEP164 functionality in a debilitating human ciliopathy.
Keywords: CEP164; TTBK2; basal body; centriole; centrosome; cilia; ciliogenesis; ciliopathy; distal appendage; nephronophthisis.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
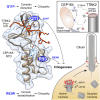

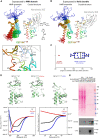


Comment in
-
How CEP164 ciliopathy mutations impair ciliogenesis.Structure. 2022 Jan 6;30(1):4-5. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2021.12.007. Structure. 2022. PMID: 34995479
References
-
- Argentaro A., Yang J.C., Chapman L., Kowalczyk M.S., Gibbons R.J., Higgs D.R., Neuhaus D., Rhodes D. Structural consequences of disease-causing mutations in the ATRX-DNMT3-DNMT3L (ADD) domain of the chromatin-associated protein ATRX. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A. 2007;104:11939–11944. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

