Comparison of three tests for latent tuberculosis infection in high-risk people in the USA: an observational cohort study
- PMID: 34499863
- PMCID: PMC8712384
- DOI: 10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00145-6
Comparison of three tests for latent tuberculosis infection in high-risk people in the USA: an observational cohort study
Abstract
Background: Treatment of latent tuberculosis infection is an important strategy to prevent tuberculosis disease. In the USA, three tests are used to identify latent tuberculosis infection: the tuberculin skin test (TST) and two IFN-γ release assays (T-SPOT.TB and QuantiFERON). To our knowledge, few large studies have compared all three tests among people at high risk of latent tuberculosis infection or progression to tuberculosis disease. We aimed to assess test agreement between IFN-γ release assays and TST to provide guidance on their use in important risk groups.
Methods: In this observational cohort study, we enrolled participants at high risk of latent tuberculosis infection or progression to tuberculosis disease at ten US sites with 18 affiliated clinics, including close contacts of infectious tuberculosis cases, people born in countries whose populations in the USA have high (≥100 cases per 100 000 people) or moderate (10-99 cases per 100 000 people) tuberculosis incidence, and people with HIV. Participants were interviewed about demographics and medical risk factors, and all three tests were administered to each participant. The primary endpoints for this study were the proportions of positive test results by test type stratified by risk group and test concordance by risk group for participants with valid results for all three test types. The study is registered at ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT01622140.
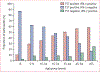
Findings: Between July 12, 2012, and May 5, 2017, 26 292 people were approached and 22 131 (84·2%) were enrolled in the study. Data from 21 846 (98·7%) participants were available for analysis, including 3790 (17·3%) born in the USA and 18 023 (82·5%) born outside the USA. Among non-US-born participants overall, the RR comparing the proportions of TST-positive results (7476 [43·2%] of 17 306 participants) to QuantiFERON-positive results (4732 [26·5%] of 17 882 participants) was 1·6 (95% CI 1·6-1·7). The risk ratio (RR) for the comparison with the proportion of T-SPOT.TB-positive results (3693 [21·6%] of 17 118 participants) was 2·0 (95% CI 1·9-2·1). US-born participants had less variation in the proportions of positive results across all tests. The RRs for the proportion of TST-positive results (391 [10·9%] of 3575 participants) compared with the proportion of QuantiFERON-positive results (445 [12·0%] of 3693 participants) and T-SPOT.TB-positive results (295 [8·1%] of 3638 participants) were 0·9 (95% CI 0·8-1·0) and 1·3 (1·2-1·6), respectively. 20 149 (91·0%) of 21 846 participants had results for all three tests, including 16 712 (76%) non-US-born participants. Discordance between TST and IFN-γ release assay results varied by age among non-US-born participants and was greatest among the 848 non-US-born children younger than 5 years. 204 (87·2%) of 234 non-US-born children younger than 5 years with at least one positive test were TST-positive and IFN-γ release assay-negative. The proportion of non-US-born participants who were TST-negative but IFN-γ release assay-positive ranged from one (0·5%) of 199 children younger than 2 years to 86 (14·5%) of 594 participants aged 65 years and older (ptrend<0·0001). Test agreement was higher between the two IFN-γ release assays than between TST and either IFN-γ release assay, regardless of birthplace. κ agreement was particularly low between TST and IFN-γ release assays in non-US-born children younger than 5 years.
Interpretation: Our findings support the preferential use of IFN-γ release assays for the diagnosis of latent tuberculosis in high-risk populations, especially in very young and older people born outside the USA.
Funding: US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests We declare no competing interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
Discordant results of tests for tuberculosis reconsidered.Lancet Infect Dis. 2022 Feb;22(2):164. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00807-0. Lancet Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 35092786 No abstract available.
-
Discordant results of tests for tuberculosis reconsidered - Authors' reply.Lancet Infect Dis. 2022 Feb;22(2):164-165. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00805-7. Lancet Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 35092787 No abstract available.
References
-
- O’Garra A, Redford PS, McNab FW, Bloom CI, Wilkinson RJ, Berry MPR. The immune response in tuberculosis. Annu Rev Immunol 2013; 31: 475–527. - PubMed