Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for infants with high-risk KMT2A gene-rearranged acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- PMID: 34500465
- PMCID: PMC8679679
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2020004157
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for infants with high-risk KMT2A gene-rearranged acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Abstract
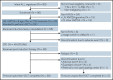
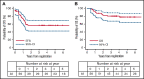
The role of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) for infants with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and KMT2A gene rearrangement (KMT2A-r) is controversial in terms of both its efficacy and potential for acute and late toxicities. In Japanese Pediatric Leukemia/Lymphoma Study Group trial MLL-10, by introducing intensive chemotherapy, indication of HSCT was restricted to patients with high-risk (HR) features only (KMT2A-r and either age <180 days or presence of central nervous system leukemia). Of the 56 HR patients, 49 achieved complete remission. Forty-three patients received HSCT in first remission including 38 patients receiving protocol-specified HSCT with conditioning consisting of individualized targeted doses of busulfan, etoposide, and cyclophosphamide. Three-year event-free survival (EFS) of 56.8% (95% confidence interval [CI], 42.4% to 68.8%) and overall survival of 80.2% (95% CI, 67.1% to 88.5%) were accomplished. Univariable analysis showed that Interfant-HR criteria and flow cytometric minimal residual disease (MRD; ≥0.01%), both at the end of induction and at the end of consolidation (EOC), were significantly associated with poorer EFS. In the multivariable analysis, positive MRD at EOC was solely associated with poor EFS (P < .001). Rapid pretransplant MRD clearance and tailored HSCT strategy in the MLL-10 trial resulted in a favorable outcome for infants with HR KMT2A-r ALL. However, considering the high rate of potentially life-threatening toxicities and the risk of late effects, its indication should be further restricted or even eliminated in the future by introducing more effective therapeutic modalities with minimal toxicities. This trial was registered at the University Hospital Medical Information Network Clinical Trials Registry (UMIN-CTR) as #UMIN000004801.
© 2021 by The American Society of Hematology.
Figures

References
-
- Tomizawa D. Recent progress in the treatment of infant acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pediatr Int. 2015;57(5):811-819. - PubMed
-
- Pieters R, Schrappe M, De Lorenzo P, et al. . A treatment protocol for infants younger than 1 year with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (Interfant-99): an observational study and a multicentre randomised trial. Lancet. 2007;370(9583):240-250. - PubMed
-
- Pieters R, De Lorenzo P, Ancliffe P, et al. . Outcome of infants younger than 1 year with acute lymphoblastic leukemia treated with the Interfant-06 protocol: results from an international phase III randomized study. J Clin Oncol. 2019;37(25):2246-2256. - PubMed
-
- Isoyama K, Eguchi M, Hibi S, et al. . Risk-directed treatment of infant acute lymphoblastic leukaemia based on early assessment of MLL gene status: results of the Japan Infant Leukaemia Study (MLL96). Br J Haematol. 2002;118(4):999-1010. - PubMed
-
- Kosaka Y, Koh K, Kinukawa N, et al. . Infant acute lymphoblastic leukemia with MLL gene rearrangements: outcome following intensive chemotherapy and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood. 2004;104(12):3527-3534. - PubMed

