α-Mangostin Nanoparticles Cytotoxicity and Cell Death Modalities in Breast Cancer Cell Lines
- PMID: 34500560
- PMCID: PMC8434247
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26175119
α-Mangostin Nanoparticles Cytotoxicity and Cell Death Modalities in Breast Cancer Cell Lines
Abstract
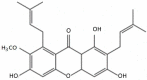
α-Mangostin (AMG) is a potent anticancer xanthone that was discovered in mangosteen (Garcinia mangostana Linn.). AMG possesses the highest opportunity for chemopreventive and chemotherapeutic therapy. AMG inhibits every step in the process of carcinogenesis. AMG suppressed multiple breast cancer (BC) cell proliferation and apoptosis by decreasing the creation of cancerous compounds. Accumulating BC abnormalities and their associated molecular signaling pathways promotes novel treatment strategies. Chemotherapy is a commonly used treatment; due to the possibility of unpleasant side effects and multidrug resistance, there has been substantial progress in searching for alternative solutions, including the use of plant-derived natural chemicals. Due to the limitations of conventional cancer therapy, nanotechnology provides hope for effective and efficient cancer diagnosis and treatment. Nanotechnology enables the delivery of nanoparticles and increased solubility of drugs and drug targeting, resulting in increased cytotoxicity and cell death during BC treatment. This review summarizes the progress and development of AMG's cytotoxicity and the mechanism of death BC cells. The combination of natural medicine and nanotechnology into a synergistic capital will provide various benefits. This information will aid in the development of AMG nanoparticle preparations and may open up new avenues for discovering an effective BC treatment.
Keywords: AMG; apoptosis; breast cancer; cell death; cytotoxicity; nanotechnology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Figures

References
-
- Van Oost V. Study of alpha mangostin as a chemoprotective agent for breast cancer via activation of the p53 pathway. Elaia. 2018;2:16.
-
- Baktiar Laskar Y., Meitei Lourembam R., Behari Mazumder P. Herbal Remedies for Breast Cancer Prevention and Treatment. Med. Plants - Use Prev. Treat. Dis. 2020:1–22. doi: 10.5772/intechopen.89669. - DOI
-
- Ullah I., Khalil A.T., Ali M., Iqbal J., Ali W., Alarifi S., Shinwari Z.K. Green-Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles Induced Apoptotic Cell Death in MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells by Generating Reactive Oxygen Species and Activating Caspase 3 and 9 Enzyme Activities. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020;2020 doi: 10.1155/2020/1215395. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

