ST-2191, an Anellated Bismorpholino Derivative of Oxy-Fingolimod, Shows Selective S1P1 Agonist and Functional Antagonist Potency In Vitro and In Vivo
- PMID: 34500564
- PMCID: PMC8433829
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26175134
ST-2191, an Anellated Bismorpholino Derivative of Oxy-Fingolimod, Shows Selective S1P1 Agonist and Functional Antagonist Potency In Vitro and In Vivo
Abstract
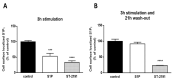
Sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) is an extensively studied signaling molecule that contributes to cell proliferation, survival, migration and other functions through binding to specific S1P receptors. The cycle of S1P1 internalization upon S1P binding and recycling to the cell surface when local S1P concentrations are low drives T cell trafficking. S1P1 modulators, such as fingolimod, disrupt this recycling by inducing persistent S1P1 internalization and receptor degradation, which results in blocked egress of T cells from the secondary lymphoid tissues. The approval of these compounds for the treatment of multiple sclerosis has placed the development of S1PR modulators in the focus of pharmacological research, mostly for autoimmune indications. Here, we report on a novel anellated bismorpholino derivative of oxy-fingolimod, named ST-2191, which exerts selective S1P1 agonist and functional antagonist potency. ST-2191 is also effective in reducing the lymphocyte number in mice, and this effect is not dependent on phosphorylation by sphingosine kinase 2 for activity. These data show that ST-2191 is a novel S1P1 modulator, but further experiments are needed to analyze the therapeutic impact of ST-2191 in animal models of autoimmune diseases.
Keywords: S1P1 receptor; ST-2191; anellated bismorpholino; functional antagonism; lymphopenia; sphingosine 1-phosphate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 310030_135619/Schweizerischer Nationalfonds zur Förderung der Wissenschaftlichen Forschung
- n.a./Schweizerische Multiple Sklerose Gesellschaft
- GRK2158, INST 208/690-1/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft
- CA15135, CA18133, CA18240/European Cooperation in Science and Technology
- 20/2020/Hochschulstiftung der Universität Bern
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

