Grief Reactions and Grief Counseling among Bereaved Chinese Individuals during COVID-19 Pandemic: Study Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial Combined with a Longitudinal Study
- PMID: 34501650
- PMCID: PMC8431533
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph18179061
Grief Reactions and Grief Counseling among Bereaved Chinese Individuals during COVID-19 Pandemic: Study Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial Combined with a Longitudinal Study
Abstract
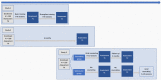
COVID-19 has caused nearly 4.3 million deaths all around the world. People who have experienced loss during this special period may find it difficult to adapt to life after loss, and may even suffer from prolonged grief disorder or other mental health problems. However, there is a huge gap of grief research in China, with almost no comprehensive grief intervention training system or very few professional grief consultants. Considering the large number of bereaved individuals who are suffering from grief and other mental health problems, it is significant to develop a suitable and effective intervention protocol immediately. This article illustrates a study protocol initiated by a Chinese university to investigate the mental health of bereaved individuals during the COVID-19 pandemic and train grief counselors to provide grief counseling to the bereaved, as well as to evaluate the effectiveness of the grief counseling. The method is as follows: (1) 300 psychological counselors will be recruited to attend the grief counseling training. Assessments will be conducted at three time points: baseline (T0), after the basic training (T1), and after the advanced training (T2); (2) 500 bereaved Chinese will be recruit to join the online survey and will be assessed at two time points with a six-month interval; and (3) a two-armed (grief counseling versus wait-list controls) RCT (random control trials) will be conducted with 160 bereaved individuals. Assessments will be conducted at three time points: before randomization (baseline, T0), at the post-counseling (T1), and three months after the post-counseling (T2). Primary outcomes will be assessed by the Prolonged Grief Questionnaire (PG-13), the 20-item PTSD Checklist for DSM-5 (PCL-5), the Depression Anxiety and Stress Scale (DASS-21), and the Posttraumatic Growth Inventory (PTGI). This research will help develop grief research and grief counseling in China, as well as provide professional mental health services for individuals who may suffer from grief-related disorders in the future.
Keywords: COVID-19 pandemic; bereavement; complicated grief; grief counseling; grief reactions; mental health; prolonged grief disorder.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
-
- World Health Organization WHO Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Dashboard. [(accessed on 18 August 2021)]; Available online: https://covid19.who.int/
-
- Bonanno G.A. The Other Side of Sadness: What the New Science of Bereavement Tells Us about Life after Loss. Basic Books; New York, NY, USA: 2009. [(accessed on 18 April 2021)]. Available online: https://search.proquest.com/books/other-side-sadness-what-new-science-be....
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous