Important Contributions to Reducing Nitrogen Oxide Emissions from Internal Combustion Engines
- PMID: 34501664
- PMCID: PMC8430564
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph18179075
Important Contributions to Reducing Nitrogen Oxide Emissions from Internal Combustion Engines
Abstract
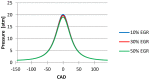
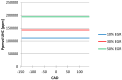
Nitrogen oxides are considered significant pollutants because of their effects on ecosystems and human health. The amount of NOx emitted by internal combustion engines can be reduced, mostly by acting on the conditions in which combustion takes place, respectively by lowering the peak flame temperature, reducing the excess of oxygen, etc. The homogeneous charge compression ignition (HCCI) engine represents a new technology that can simultaneously reduce NOx emissions and fuel consumption. This article presents these benefits of the HCCI engine by comparing the emissions and fuel consumption of a monocylinder engine when it is operated in a conventional way, with spark ignition, with those obtained when the engine is running in the HCCI mode. Moreover, since engine simulation has become an important tool for investigating the HCCI process and for developing new control strategies for it, this was used in this study to determine the effects of the exhaust gas recirculation on the combustion quality, respectively, on emissions.
Keywords: combustion dioxide; emissions; risks.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- WHO . WHO; [(accessed on 25 May 2021)]. Air Pollution. Available online: http://www.who.int/airpollution/en/
-
- Burr M., Gregory C. Vehicular exhaust. Encylopedia Environ. Health. 2011;49:563–645.
-
- Whichmann H.E. Environmental pollutants: Diesel exhaust particles. Encyclopedia Respir. Med. 2006;1:96–100.
-
- Statescu C., Honceriu C., Jurcau R.N., Trus C. An Original Study on the Correlations between Magnesium and Depression and their Cardiovascular Relevance. Rev. Chim. 2019;70:4102–4104. doi: 10.37358/RC.19.11.7711. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

