Enzyme Therapy: Current Challenges and Future Perspectives
- PMID: 34502086
- PMCID: PMC8431097
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22179181
Enzyme Therapy: Current Challenges and Future Perspectives
Abstract
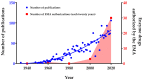
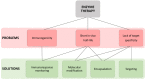
In recent years, enzymes have risen as promising therapeutic tools for different pathologies, from metabolic deficiencies, such as fibrosis conditions, ocular pathologies or joint problems, to cancer or cardiovascular diseases. Treatments based on the catalytic activity of enzymes are able to convert a wide range of target molecules to restore the correct physiological metabolism. These treatments present several advantages compared to established therapeutic approaches thanks to their affinity and specificity properties. However, enzymes present some challenges, such as short in vivo half-life, lack of targeted action and, in particular, patient immune system reaction against the enzyme. For this reason, it is important to monitor serum immune response during treatment. This can be achieved by conventional techniques (ELISA) but also by new promising tools such as microarrays. These assays have gained popularity due to their high-throughput analysis capacity, their simplicity, and their potential to monitor the immune response of patients during enzyme therapies. In this growing field, research is still ongoing to solve current health problems such as COVID-19. Currently, promising therapeutic alternatives using the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) are being studied to treat COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; biotechnology; encapsulation; enzyme therapy; microarray; molecular modification of enzymes; monitoring of immune response.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

