Cytokines and Chemokines Involved in Osteoarthritis Pathogenesis
- PMID: 34502117
- PMCID: PMC8431625
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22179208
Cytokines and Chemokines Involved in Osteoarthritis Pathogenesis
Abstract
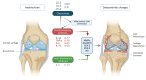
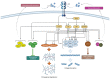
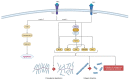
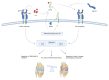
Osteoarthritis is a common cause of disability worldwide. Although commonly referred to as a disease of the joint cartilage, osteoarthritis affects all joint tissues equally. The pathogenesis of this degenerative process is not completely understood; however, a low-grade inflammation leading to an imbalance between anabolic and katabolic processes is a well-established factor. The complex network of cytokines regulating these processes and cell communication has a central role in the development and progression of osteoarthritis. Concentrations of both proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines were found to be altered depending on the osteoarthritis stage and activity. In this review, we analyzed individual cytokines involved in the immune processes with an emphasis on their function in osteoarthritis.
Keywords: biomarker; chemokines; cytokines; inflammation; osteoarthritis; pathogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

