Cripto-1 as a Key Factor in Tumor Progression, Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition and Cancer Stem Cells
- PMID: 34502188
- PMCID: PMC8430685
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22179280
Cripto-1 as a Key Factor in Tumor Progression, Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition and Cancer Stem Cells
Abstract
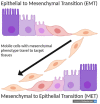
Cripto-1 is an essential protein for human development that plays a key role in the early phase of gastrulation in the differentiation of an embryo as well as assists with wound healing processes. Importantly, Cripto-1 induces epithelial to mesenchymal transition to turn fixed epithelial cells into a more mobile mesenchymal phenotype through the downregulation of epithelial adhesion molecules such as E-cadherin, occludins, and claudins, and the upregulation of mesenchymal, mobile proteins, such as N-cadherin, Snail, and Slug. Consequently, Cripto-1's role in inducing EMT to promote cell motility is beneficial in embryogenesis, but detrimental in the formation, progression and metastasis of malignant tumors. Indeed, Cripto-1 is found to be upregulated in most cancers, such as breast, lung, gastrointestinal, hepatic, renal, cervical, ovarian, prostate, and skin cancers. Through its role in EMT, Cripto-1 can remodel cancer cells to enable them to travel through the extracellular matrix as well as blood and lymphatic vessels to metastasize to different organs. Additionally, Cripto-1 promotes the survival of cancer stem cells, which can lead to relapse in cancer patients.
Keywords: Cripto-1; EMT; biomarker; breast cancer; cancer stem cells; epithelial to mesenchymal transition; melanoma; metastasis; therapeutic target; tumor progression.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Morkel M., Huelsken J., Wakamiya M., Ding J., van de Wetering M., Clevers H., Taketo M.M., Behringer R.R., Shen M.M., Birchmeier W. Beta catenin regulates Cripto- and Wnt3-dependent gene expression programs in mouse axis and mesoderm formation. Development. 2003;130:6283–6294. doi: 10.1242/dev.00859. - DOI - PubMed
-
- D’Aniello C., Lonardo E., Iaconis S., Guardiola O., Liguoro A.M., Liguori G.L., Autiero M., Carmeliet P., Minchiotti G. G protein-coupled receptor APJ and its ligand apelin act downstream of Cripto to specify embryonic stem cells toward the cardiac lineage through extracellular signal-regulated kinase/p70S6 kinase signaling pathway. Circ. Res. 2009;105:231–238. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.109.201186. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials