Deciphering the Potential Neuroprotective Effects of Luteolin against Aβ1-42-Induced Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 34502488
- PMCID: PMC8430819
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22179583
Deciphering the Potential Neuroprotective Effects of Luteolin against Aβ1-42-Induced Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
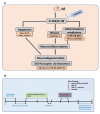
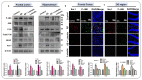
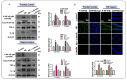
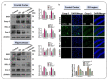
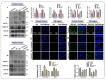
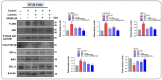
The current study was undertaken to unveil the protective effects of Luteolin, a natural flavonoid, against amyloid-beta (Aβ1-42)-induced neuroinflammation, amyloidogenesis, and synaptic dysfunction in mice. For the development of an AD mouse model, amyloid-beta (Aβ1-42, 5 μL/5 min/mouse) oligomers were injected intracerebroventricularly (i.c.v.) into mice's brain by using a stereotaxic frame. After that, the mice were treated with Luteolin for two weeks at a dose of 80 mg/kg/day. To monitor the biochemical changes, we conducted western blotting and immunofluorescence analysis. According to our findings, the infusion of amyloid-beta activated c-Jun N-terminal kinases (p-JNK), p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases, glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), and ionized calcium adaptor molecule 1 (Iba-1) in the cortex and hippocampus of the experimental mice; these changes were significantly inhibited in Aβ1-42 + Luteolin-treated mice. Likewise, we also checked the expression of inflammatory markers, such as p-nuclear factor-kB p65 (p-NF-kB p65 (Ser536), tissue necrosis factor (TNF-α), and Interleukin1-β (IL-1β), in Aβ1-42-injected mice brain, which was attenuated in Aβ1-42 + Luteolin-treated mice brains. Further, we investigated the expression of pro- and anti-apoptotic cell death markers such as Bax, Bcl-2, Caspase-3, and Cox-2, which was significantly reduced in Aβ1-42 + Lut-treated mice brains compared to the brains of the Aβ-injected group. The results also indicated that with the administration of Aβ1-42, the expression levels of β-site amyloid precursor protein cleaving enzyme (BACE-1) and amyloid-beta (Aβ1-42) were significantly enhanced, while they were reduced in Aβ1-42 + Luteolin-treated mice. We also checked the expression of synaptic markers such as PSD-95 and SNAP-25, which was significantly enhanced in Aβ1-42 + Lut-treated mice. To unveil the underlying factors responsible for the protective effects of Luteolin against AD, we used a specific JNK inhibitor, which suggested that Luteolin reduced Aβ-associated neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration via inhibition of JNK. Collectively, our results indicate that Luteolin could serve as a novel therapeutic agent against AD-like pathological changes in mice.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; amyloid-beta; luteolin; neurodegeneration; neuroprotection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oral Administration of Alpha Linoleic Acid Rescues Aβ-Induced Glia-Mediated Neuroinflammation and Cognitive Dysfunction in C57BL/6N Mice.Cells. 2020 Mar 9;9(3):667. doi: 10.3390/cells9030667. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32182943 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidative and Anti-inflammatory Effects of Kojic Acid in Aβ-Induced Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease.Mol Neurobiol. 2021 Oct;58(10):5127-5140. doi: 10.1007/s12035-021-02460-4. Epub 2021 Jul 13. Mol Neurobiol. 2021. PMID: 34255249
-
Adalimumab improves cognitive impairment, exerts neuroprotective effects and attenuates neuroinflammation in an Aβ1-40-injected mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Cytotherapy. 2019 Jun;21(6):671-682. doi: 10.1016/j.jcyt.2019.04.054. Epub 2019 May 7. Cytotherapy. 2019. PMID: 31076196
-
Protection against Alzheimer's disease by luteolin: Role of brain glucose regulation, anti-inflammatory activity, and the gut microbiota-liver-brain axis.Biofactors. 2021 Mar;47(2):218-231. doi: 10.1002/biof.1703. Epub 2020 Dec 21. Biofactors. 2021. PMID: 33347668 Review.
-
Neuroprotective effects and possible mechanisms of berberine in animal models of Alzheimer's disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jan 8;14:1287750. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1287750. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38259291 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Anti-Neuroinflammatory Potential of Natural Products in the Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease.Molecules. 2023 Feb 3;28(3):1486. doi: 10.3390/molecules28031486. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36771152 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polyphenols, Alkaloids, and Terpenoids Against Neurodegeneration: Evaluating the Neuroprotective Effects of Phytocompounds Through a Comprehensive Review of the Current Evidence.Metabolites. 2025 Feb 13;15(2):124. doi: 10.3390/metabo15020124. Metabolites. 2025. PMID: 39997749 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lupeol protect against LPS-induced neuroinflammation and amyloid beta in adult mouse hippocampus.Front Nutr. 2024 Jul 10;11:1414696. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1414696. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39050141 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the mechanism of luteolin by regulating microglia polarization based on network pharmacology and in vitro experiments.Sci Rep. 2023 Aug 23;13(1):13767. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-41101-9. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37612462 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin E Analog Trolox Attenuates MPTP-Induced Parkinson's Disease in Mice, Mitigating Oxidative Stress, Neuroinflammation, and Motor Impairment.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 9;24(12):9942. doi: 10.3390/ijms24129942. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37373089 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ali M., Muhammad S., Shah M.R., Khan A., Rashid U., Farooq U., Ullah F., Sadiq A., Ayaz M., Ali M., et al. Neurologically Potent Molecules from Crataegus oxyacantha; Isolation, Anticholinesterase Inhibition, and Molecular Docking. Front. Pharmacol. 2017;8:327. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00327. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

