The Knockout of Enterobactin-Related Gene in Pectobacterium atrosepticum Results in Reduced Stress Resistance and Virulence towards the Primed Plants
- PMID: 34502502
- PMCID: PMC8431002
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22179594
The Knockout of Enterobactin-Related Gene in Pectobacterium atrosepticum Results in Reduced Stress Resistance and Virulence towards the Primed Plants
Abstract
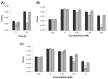
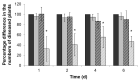
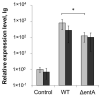
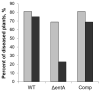
Siderophores produced by microorganisms to scavenge iron from the environment have been shown to contribute to virulence and/or stress resistance of some plant pathogenic bacteria. Phytopathogenic bacteria of Pectobacterium genus possess genes for the synthesis of siderophore enterobactin, which role in plant-pathogen interactions has not been elucidated. In the present study we characterized the phenotype of the mutant strain of Pba deficient for the enterobactin-biosynthetic gene entA. We showed that enterobactin may be considered as a conditionally beneficial virulence factor of Pba. The entA knockout did not reduce Pba virulence on non-primed plants; however, salicylic acid-primed plants were more resistant to ΔentA mutant than to the wild type Pba. The reduced virulence of ΔentA mutant towards the primed plants is likely explained by its compromised resistance to oxidative stress.
Keywords: Pectobacterium; enterobactin; oxidative stress; priming; salicylic acid; siderophores; virulence factors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Structure-Functional Characteristics of the Svx Protein-The Virulence Factor of the Phytopathogenic Bacterium Pectobacterium atrosepticum.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 21;23(13):6914. doi: 10.3390/ijms23136914. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35805920 Free PMC article.
-
Enterobactin as Part of the Oxidative Stress Response Repertoire.PLoS One. 2016 Jun 16;11(6):e0157799. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157799. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27310257 Free PMC article.
-
Variation in siderophore biosynthetic gene distribution and production across environmental and faecal populations of Escherichia coli.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 10;10(3):e0117906. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0117906. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25756870 Free PMC article.
-
Salmochelin, the long-overlooked catecholate siderophore of Salmonella.Biometals. 2009 Aug;22(4):691-5. doi: 10.1007/s10534-009-9217-4. Epub 2009 Feb 13. Biometals. 2009. PMID: 19214756 Review.
-
How pathogenic bacteria evade mammalian sabotage in the battle for iron.Nat Chem Biol. 2006 Mar;2(3):132-8. doi: 10.1038/nchembio771. Nat Chem Biol. 2006. PMID: 16485005 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Heat Shock Protein (Hsp) Chaperones in Environmental Stress Adaptation and Virulence of Plant Pathogenic Bacteria.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 9;26(2):528. doi: 10.3390/ijms26020528. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39859244 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of Homologous Recombination on Core Genome Evolution and Host Adaptation of Pectobacterium parmentieri.Genome Biol Evol. 2024 Mar 2;16(3):evae032. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evae032. Genome Biol Evol. 2024. PMID: 38385549 Free PMC article.
-
Svx Peptidases of Phytopathogenic Pectolytic Bacteria: Structural, Catalytic and Phytoimmune Properties.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 7;25(2):756. doi: 10.3390/ijms25020756. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38255830 Free PMC article.
-
A novel phytopathogen Erwinia sorbitola sp. nov., isolated from the feces of ruddy shelducks.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Feb 16;13:1109634. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1109634. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36875519 Free PMC article.
-
Importance of microbial amphiphiles: interaction potential of biosurfactants, amyloids, and other exo-polymeric-substances.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 Sep 25;39(11):320. doi: 10.1007/s11274-023-03751-9. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37747579 Review.
References
-
- Charkowski A., Blanco C., Condemine G., Expert D., Franza T., Hayes C., Hugouvieux-Cotte-Pattat N., Solanilla E.L., Low D., Moleleki L., et al. The role of secretion systems and small molecules in soft-rot Enterobacteriaceae pathogenicity. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2012;50:425–449. doi: 10.1146/annurev-phyto-081211-173013. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Corbett M., Virtue S., Bell K., Birch P., Burr T., Hyman L., Lilley K., Poock S., Toth I., Salmond G. Identification of a new quorum-sensing-controlled virulence factor in Erwinia carotovora subsp. atroseptica secreted via the type II targeting pathway. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2005;18:334–342. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-18-0334. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pemberton C.L., Whitehead N.A., Sebaihia M., Bell K.S., Hyman L.J., Harris S.J., Matlin A.J., Robson N.D., Birch P.R.J., Carr J.P., et al. Novel quorum-sensing-controlled genes in Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora: Identification of a fungal elicitor homologue in a soft-rotting bacterium. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2005;18:343–353. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-18-0343. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ageichik A.V., Evtushenkov A.N., Nikolaichik E.A. The role of type III secretion system in Erwinia carotovora subsp. atroseptica virulence. Plant Protect. Sci. 2002;38:523–527. doi: 10.17221/10544-PPS. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

