External Validation of a Nomogram to Predict Survival and Benefit of Concurrent Chemoradiation for Stage II Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
- PMID: 34503096
- PMCID: PMC8428339
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13174286
External Validation of a Nomogram to Predict Survival and Benefit of Concurrent Chemoradiation for Stage II Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
Abstract
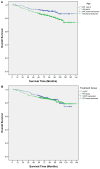
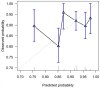
A nomogram was recently published by Sun et al. to predict overall survival (OS) and the additional benefit of concurrent chemoradiation (CCRT) vs. radiotherapy (RT) alone, in stage II NPC treated with conventional RT. We aimed to assess the predictors of OS and to externally validate the nomogram in the IMRT era. We analyzed stage II NPC patients treated with definitive RT alone or CCRT between 2001 and 2011 under the territory-wide Hong Kong NPC Study Group 1301 study. Clinical parameters were studied using the Cox proportional hazards model to estimate OS. The nomogram by Sun et al. was applied with 1000 times bootstrap resampling to calculate the concordance index, and we compared the nomogram predicted and observed 5-year OS. There were 482 patients included. The 5-year OS was 89.0%. In the multivariable analysis, an age > 45 years was the only significant predictor of OS (HR, 1.98; 95%CI, 1.15-3.44). Other clinical parameters were insignificant, including the use of CCRT (HR, 0.99; 95%CI, 0.62-1.58). The nomogram yielded a concordance index of 0.55 (95% CI, 0.49-0.62) which lacked clinically meaningful discriminative power. The nomogram proposed by Sun et al. should be interpreted with caution when applied to stage II NPC patients in the IMRT era. The benefit of CCRT remained controversial.
Keywords: chemotherapy; nasopharyngeal carcinoma; nomogram; radiotherapy; survival.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Nasopharynx. [(accessed on 21 February 2021)]; Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/data/factsheets/cancers/4-Nasopharynx-fact-she....
-
- Hong Kong Cancer Registry, H.A. Nasopharyngeal Cancer in 2017. [(accessed on 21 February 2021)]; Available online: https://www3.ha.org.hk/cancereg/pdf/factsheet/2017/npc_2017.pdf.
-
- Hong Kong Cancer Registry, H.A. Nasopharyngeal Cancer in 2018. [(accessed on 21 February 2021)]; Available online: https://www3.ha.org.hk/cancereg/pdf/factsheet/2018/npc_2018.pdf.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

