Evaluation of Antibody Responses to COVID-19 Vaccines among Solid Tumor and Hematologic Patients
- PMID: 34503127
- PMCID: PMC8430869
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13174312
Evaluation of Antibody Responses to COVID-19 Vaccines among Solid Tumor and Hematologic Patients
Abstract
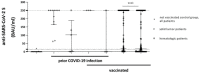
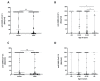
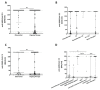
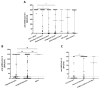
Vaccination is the primary public health strategy to cope with the COVID-19 pandemic. Although solid tumor and hematologic patients are at higher risk of serious COVID-19-related complications, data on immune responses to COVID-19 vaccines in this patient cohort are particularly scarce. The present study, therefore, aimed at the standardized determination of anti-SARS-CoV-2 spike protein antibody titers among non-vaccinated versus vaccinated solid tumor and hematologic patients who are under clinical observation or under treatment at the University Hospital Krems. Standardized anti-SARS-CoV-2 S antibody titers of a total of 441 patients were retrospectively analyzed. Our results show that antibody titers against the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein are significantly higher in solid tumor versus hematologic patients. While SARS-CoV-2 antibody titers were equal among sexes, an age-dependent decrease was observed. Of note, our studies additionally show that complete vaccination represents a valuable predictor for high anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody responses in solid tumor and hematologic patients. In summary, to date, this is one of the largest studies to comprehensively evaluate the impact of various COVID-19 vaccines on anti-SARS-CoV-2 S antibody production in solid tumor and hematologic patients. Our findings aim to support future vaccination strategies in these highly vulnerable patients, including vaccination booster programs and alternative protective approaches.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; SARS-CoV-2 S vaccine; antibody response; cancer patients.
Conflict of interest statement
J.S. declares honorarium payments from Abbvie, Amgen, Gilead, Janssen, Merck, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche and Servier as an invited speaker or expert consulting on other topics than SARS-CoV-2 and vaccination. K.H. declares honorarium from Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim and Roche as an expert consulting on other topics than SARS-CoV-2 and vaccination. M.P. declares financial support from Roche for research projects other than SARS-CoV-2 and vaccination. S.V. received speaker’s honoraria from Bristol Myers Squibb, MSD, Pfizer and consultancy fees from Roche, Eusa, MSD and Merck on other topics than SARS-CoV-2 and vaccination. K.P. has received speaker’s honoraria from Celgene, Amgen Inc. and Janssen Pharmaceuticals, consultancy fees from Celgene, Takeda and Janssen Pharmaceuticals and research support from Roche Pharmaceuticals on other topics than SARS-CoV-2 and vaccination. All other authors have no conflict of interest with regard to this work.
Figures
References
-
- Voysey M., Clemens S.A.C., Madhi S.A., Weckx L.Y., Folegatti P.M., Aley P.K., Angus B., Baillie V.L., Barnabas S.L., Bhorat Q.E., et al. Safety and efficacy of the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine (AZD1222) against SARS-CoV-2: An interim analysis of four randomised controlled trials in Brazil, South Africa, and the UK. Lancet. 2021;397:99–111. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32661-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

