Young-onset type 2 diabetes in South Korea: a review of the current status and unmet need
- PMID: 34503316
- PMCID: PMC8435510
- DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2021.379
Young-onset type 2 diabetes in South Korea: a review of the current status and unmet need
Abstract
The prevalence of young-onset (diagnosis at age < 40 years) type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is increasing globally. Young-onset T2DM has a common pathophysiology of glucose dysregulation as in late-onset T2DM. However, it presents a greater association with obesity and a more rapid decline in β-cell function than late-onset T2DM. Accumulating evidence indicates that disease progression in young-onset T2DM is rapid, resulting in early and frequent development of microvascular and macrovascular complications, as well as premature death. Improper management and low adherence to medical therapy are important issues in young-onset T2DM. This review discusses the epidemiology, disease entity, and clinical issues associated with young-onset T2DM. We also present the prevalence and clinical characteristics of patients with young-onset T2DM in South Korea.
Keywords: Diabetes complications; Diabetes mellitus, type 2; Epidemiology; Treatment adherence and compliance; Young adult.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
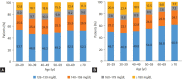
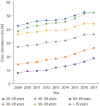
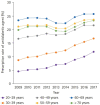
References
-
- Magliano DJ, Sacre JW, Harding JL, Gregg EW, Zimmet PZ, Shaw JE. Young-onset type 2 diabetes mellitus: implications for morbidity and mortality. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2020;16:321–331. - PubMed
-
- International Diabetes Federation . IDF Diabetes Atlas. 6th ed. Brussels (BE): International Diabetes Federation; 2013.
-
- Lascar N, Brown J, Pattison H, Barnett AH, Bailey CJ, Bellary S. Type 2 diabetes in adolescents and young adults. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018;6:69–80. - PubMed
-
- Ke C, Sohal P, Qian H, Quan H, Khan NA. Diabetes in the young: a population-based study of South Asian, Chinese and White people. Diabet Med. 2015;32:487–496. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
