Accelerated functional brain aging in pre-clinical familial Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 34504080
- PMCID: PMC8429427
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-25492-9
Accelerated functional brain aging in pre-clinical familial Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
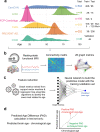
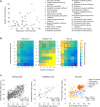
Resting state functional connectivity (rs-fMRI) is impaired early in persons who subsequently develop Alzheimer's disease (AD) dementia. This impairment may be leveraged to aid investigation of the pre-clinical phase of AD. We developed a model that predicts brain age from resting state (rs)-fMRI data, and assessed whether genetic determinants of AD, as well as beta-amyloid (Aβ) pathology, can accelerate brain aging. Using data from 1340 cognitively unimpaired participants between 18-94 years of age from multiple sites, we showed that topological properties of graphs constructed from rs-fMRI can predict chronological age across the lifespan. Application of our predictive model to the context of pre-clinical AD revealed that the pre-symptomatic phase of autosomal dominant AD includes acceleration of functional brain aging. This association was stronger in individuals having significant Aβ pathology.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Franke K, Ziegler G, Klöppel S, Gaser C, Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Estimating the age of healthy subjects from T1-weighted MRI scans using kernel methods: exploring the influence of various parameters. Neuroimage. 2010;50:883–892. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.01.005. - DOI - PubMed

