Interaction of MS prevalence, radon gas concentration, and patient nutrition: a case-control study
- PMID: 34504114
- PMCID: PMC8429741
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-96816-4
Interaction of MS prevalence, radon gas concentration, and patient nutrition: a case-control study
Abstract
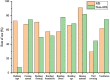
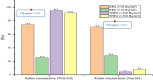
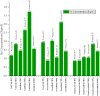
In general, ecological findings indicate a positive correlation between MS and the intake of certain foods. This study aimed to investigate the relationship between radon (Rn) gas concentration and nutrition of patients in food groups with MS. Demographic information, diet, and building characteristics were collected by a questionnaire. Indoors Rn gas was measured using CR-39 detectors. Three models were used in the study of food intake. The interaction analysis between MS prevalence, diet, residential building characteristics, and Rn gas content was performed using SPSS 2020. The total Rn was significantly associated with cooling devices (P = 0.021). Buildings > 20 years had higher Rn concentrations than buildings < 20 years (P = 0.038). Also, no significant relationship was found between Rn-total and MS concentrations, but the total Rn concentration was higher in people homes with MS. Case group used more processed meat than the control (P < 0.001). The case group consumed more butter than the control, which was significant in Model III (P < 0.04). Tomato consumption in the case group was significantly higher than the control (P < 0.03). According to the results there was no interaction between Rn gas concentration in any of the food groups in each cases. However, future studies with larger sample sizes will be needed prospectively.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The relationship of indoor radon gas concentration with multiple sclerosis: a case-control study.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020 May;27(14):16350-16361. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-08147-y. Epub 2020 Mar 2. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32124296
-
Is there a relationship between homes' radon gas of MS and non-MS individuals, and the patients' paraclinical magnetic resonance imaging and visually evoked potentials in Yazd-Iran?Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2021 Feb;28(7):8907-8914. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-10580-y. Epub 2020 Oct 19. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2021. PMID: 33078352
-
Radon in homes and risk of lung cancer: collaborative analysis of individual data from 13 European case-control studies.BMJ. 2005 Jan 29;330(7485):223. doi: 10.1136/bmj.38308.477650.63. Epub 2004 Dec 21. BMJ. 2005. PMID: 15613366 Free PMC article.
-
Nationwide indoor 222Rn and 220Rn map for India: a review.J Environ Radioact. 2011 Nov;102(11):975-86. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvrad.2011.06.009. Epub 2011 Jul 19. J Environ Radioact. 2011. PMID: 21775033 Review.
-
A Review of Indoor and Outdoor Radon Equilibrium Factors-part II: 220Rn.Health Phys. 2018 Oct;115(4):500-506. doi: 10.1097/HP.0000000000000910. Health Phys. 2018. PMID: 30148815 Review.
Cited by
-
Everyday home radon exposure is associated with altered structural brain morphology in youths.Neurotoxicology. 2024 May;102:114-120. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2024.04.007. Epub 2024 May 3. Neurotoxicology. 2024. PMID: 38703899 Free PMC article.
-
Short-term exposure to some heavy metals carried with PM10 and cardiovascular system biomarkers during dust storm.Sci Rep. 2023 Apr 15;13(1):6146. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-31978-x. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37061544 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbasnezhad A. Environmental IMPACTS and Implications of The Radon-222, and its Urgency Attention in Iran. Geology Department Shahid Bahonar University; 2003. pp. 76175–77133.
-
- Montazerabadi, A., Ahmadian, M., Vahed, M., Yousefi, N., Fatehizadeh, A., Borhani, P., et al. Evaluation of 222 RN rate in medical dormitory of Kerman City (2012).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical