Flow estimation solely from image data through persistent homology analysis
- PMID: 34504173
- PMCID: PMC8429714
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-97222-6
Flow estimation solely from image data through persistent homology analysis
Abstract
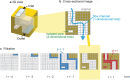
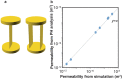
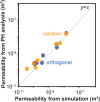
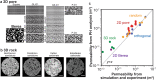
Topological data analysis is an emerging concept of data analysis for characterizing shapes. A state-of-the-art tool in topological data analysis is persistent homology, which is expected to summarize quantified topological and geometric features. Although persistent homology is useful for revealing the topological and geometric information, it is difficult to interpret the parameters of persistent homology themselves and difficult to directly relate the parameters to physical properties. In this study, we focus on connectivity and apertures of flow channels detected from persistent homology analysis. We propose a method to estimate permeability in fracture networks from parameters of persistent homology. Synthetic 3D fracture network patterns and their direct flow simulations are used for the validation. The results suggest that the persistent homology can estimate fluid flow in fracture network based on the image data. This method can easily derive the flow phenomena based on the information of the structure.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Renard P, de Marsily G. Calculating equivalent permeability: A review. Adv. Water Resour. 1997;20:253–278. doi: 10.1016/S0309-1708(96)00050-4. - DOI
-
- Costa A. Permeability-porosity relationship: A reexamination of the Kozeny–Carman equation based on a fractal pore-space geometry assumption. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006;33:1–5. doi: 10.1029/2005GL025134. - DOI
-
- Carman PC. Fluid flow through granular beds. Trans. Chem. Eng. 1937;15:S32–S48.
-
- Zimmerman RW, Bodvarsson GS. Effective transmissivity of two-dimensional fracture networks. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Geomech. Abstr. 1996;33:433–438. doi: 10.1016/0148-9062(95)00067-4. - DOI
-
- Snow D. Anisotropic permeability of fractured media. Water Resour. Res. 1969;5:1273–1289. doi: 10.1029/WR005i006p01273. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

