The impact of CASR A990G polymorphism in response to cinacalcet treatment in hemodialysis patients with secondary hyperparathyroidism
- PMID: 34504264
- PMCID: PMC8429569
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-97587-8
The impact of CASR A990G polymorphism in response to cinacalcet treatment in hemodialysis patients with secondary hyperparathyroidism
Abstract
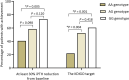
The objective of this study was to determine the impact of calcium sensing receptor (CASR) A990G genetic polymorphism on parathyroid hormone (PTH) lowering response to cinacalcet treatment when controlling for significant influencing clinical factors. This retrospective study was conducted on 135 Thai hemodialysis (HD) patients with secondary hyperparathyroidism (SHPT). CASR A990G genotypes were determined. The patients were identified as either G carriers (heterozygous or homozygous CASR 990G allele carriers) or noncarriers (homozygous CASR 990A carriers). Tested covariates were baseline PTH level (bPTH), baseline serum phosphate (bPhos), baseline serum calcium (bCa), baseline calcitriol equivalent dose (bCtriol), baseline ergocalciferol dose (bErgo), and age. The ANCOVA showed that intact PTH levels after 12 weeks of cinacalcet treatment (PTHw12) was significantly lower among G carriers compared with noncarriers after controlling for bPTH, bPhos, bCtriol, and bErgo (F(1, 127) = 15.472, p < 0.001), with the adjusted mean difference of 253.7 pg/mL. The logistic regression analysis revealed that the odds of a G carrier achieving 30% PTH reduction after 12-week cinacalcet treatment were 3.968 times greater than the odds for a noncarrier after adjusting for bPhos, bCtriol, and age. In conclusion, the CASR A990G polymorphism significantly influences cinacalcet response in HD patients with SHPT.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

