A Novel Bifunctional Fusion Protein, Vunakizumab-IL22, for Protection Against Pulmonary Immune Injury Caused by Influenza Virus
- PMID: 34504501
- PMCID: PMC8421727
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.727941
A Novel Bifunctional Fusion Protein, Vunakizumab-IL22, for Protection Against Pulmonary Immune Injury Caused by Influenza Virus
Abstract
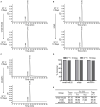
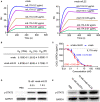
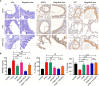
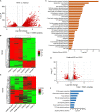
Influenza A virus infection is usually associated with acute lung injury, which is typically characterized by tracheal mucosal barrier damage and an interleukin 17A (IL-17A)-mediated inflammatory response in lung tissues. Although targeting IL-17A has been proven to be beneficial for attenuating inflammation around lung cells, it still has a limited effect on pulmonary tissue recovery after influenza A virus infection. In this research, interleukin 22 (IL-22), a cytokine involved in the repair of the pulmonary mucosal barrier, was fused to the C-terminus of the anti-IL-17A antibody vunakizumab to endow the antibody with a tissue recovery function. The vunakizumab-IL22 (vmab-IL-22) fusion protein exhibits favorable stability and retains the biological activities of both the anti-IL-17A antibody and IL-22 in vitro. Mice infected with lethal H1N1 influenza A virus and treated with vmab-mIL22 showed attenuation of lung index scores and edema when compared to those of mice treated with saline or vmab or mIL22 alone. Our results also illustrate that vmab-mIL22 triggers the upregulation of MUC2 and ZO1, as well as the modulation of cytokines such as IL-1β, HMGB1 and IL-10, indicating the recovery of pulmonary goblet cells and the suppression of excessive inflammation in mice after influenza A virus infection. Moreover, transcriptome profiling analysis suggest the downregulation of fibrosis-related genes and signaling pathways, including genes related to focal adhesion, the inflammatory response pathway, the TGF-β signaling pathway and lung fibrosis upon vmab-mIL22 treatment, which indicates that the probable mechanism of vmab-mIL22 in ameliorating H1N1 influenza A-induced lung injury. Our results reveal that the bifunctional fusion protein vmab-mIL22 can trigger potent therapeutic effects in H1N1-infected mice by enhancing lung tissue recovery and inhibiting pulmonary inflammation, which highlights a potential approach for treating influenza A virus infection by targeting IL-17A and IL-22 simultaneously.
Keywords: H1N1 influenza A virus; IL-17A; IL-22; anti-inflammatory effects; bifunctional fusion protein; lung injury; tissue repair.
Copyright © 2021 Han, Shi, Zeng, Cen, Mei, Fan, Ju and Zhu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

