Radioactive Beams for Image-Guided Particle Therapy: The BARB Experiment at GSI
- PMID: 34504803
- PMCID: PMC8422860
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.737050
Radioactive Beams for Image-Guided Particle Therapy: The BARB Experiment at GSI
Abstract
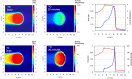
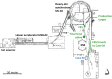
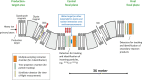
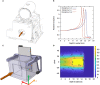
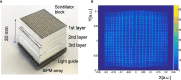
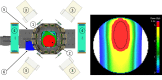
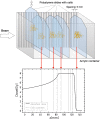
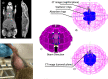
Several techniques are under development for image-guidance in particle therapy. Positron (β+) emission tomography (PET) is in use since many years, because accelerated ions generate positron-emitting isotopes by nuclear fragmentation in the human body. In heavy ion therapy, a major part of the PET signals is produced by β+-emitters generated via projectile fragmentation. A much higher intensity for the PET signal can be obtained using β+-radioactive beams directly for treatment. This idea has always been hampered by the low intensity of the secondary beams, produced by fragmentation of the primary, stable beams. With the intensity upgrade of the SIS-18 synchrotron and the isotopic separation with the fragment separator FRS in the FAIR-phase-0 in Darmstadt, it is now possible to reach radioactive ion beams with sufficient intensity to treat a tumor in small animals. This was the motivation of the BARB (Biomedical Applications of Radioactive ion Beams) experiment that is ongoing at GSI in Darmstadt. This paper will present the plans and instruments developed by the BARB collaboration for testing the use of radioactive beams in cancer therapy.
Keywords: PET; carbon ions; oxygen ions; particle therapy; radioactive ion beams.
Copyright © 2021 Boscolo, Kostyleva, Safari, Anagnostatou, Äystö, Bagchi, Binder, Dedes, Dendooven, Dickel, Drozd, Franczack, Geissel, Gianoli, Graeff, Grahn, Greiner, Haettner, Haghani, Harakeh, Horst, Hornung, Hucka, Kalantar-Nayestanaki, Kazantseva, Kindler, Knöbel, Kuzminchuk-Feuerstein, Lommel, Mukha, Nociforo, Ishikawa, Lovatti, Nitta, Ozoemelam, Pietri, Plaß, Prochazka, Purushothaman, Reidel, Roesch, Schirru, Schuy, Sokol, Steinsberger, Tanaka, Tanihata, Thirolf, Tinganelli, Voss, Weber, Weick, Winfield, Winkler, Zhao, Scheidenberger, Parodi, Durante and the Super-FRS Experiment Collaboration.
Conflict of interest statement
Author AP was employed by company MedAuston GmbH. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Depth dose measurements in water for 11C and 10C beams with therapy relevant energies.Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res A. 2022 Nov 11;1043:167464. doi: 10.1016/j.nima.2022.167464. Epub 2022 Oct 1. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res A. 2022. PMID: 36345417 Free PMC article.
-
Precision of the PET activity range during irradiation with10C,11C, and12C beams.Phys Med Biol. 2022 Dec 19;68(1). doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/aca5e8. Phys Med Biol. 2022. PMID: 36533621
-
Radioactive Beams in Particle Therapy: Past, Present, and Future.Front Phys. 2020 Aug 28;8:00326. doi: 10.3389/fphy.2020.00326. Front Phys. 2020. PMID: 33224941 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear structure opportunities with GeV radioactive beams at FAIR.Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2024 Jul 23;382(2275):20230121. doi: 10.1098/rsta.2023.0121. Epub 2024 Jun 24. Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2024. PMID: 38910400 Review.
-
Radiotherapy with heavy ions: radiobiology, clinical indications and experience at GSI, Darmstadt.Tumori. 1998 Mar-Apr;84(2):200-4. doi: 10.1177/030089169808400217. Tumori. 1998. PMID: 9620245 Review.
Cited by
-
Feasibility study of 4D-online monitoring of density gradients induced by lung cancer treatment using carbon ions.Front Oncol. 2025 Feb 26;15:1502960. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1502960. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40078180 Free PMC article.
-
Potential benefits of using radioactive ion beams for range margin reduction in carbon ion therapy.Sci Rep. 2022 Dec 16;12(1):21792. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-26290-z. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36526710 Free PMC article.
-
Experience and new prospects of PET imaging for ion beam therapy monitoring.Z Med Phys. 2023 Feb;33(1):22-34. doi: 10.1016/j.zemedi.2022.11.001. Epub 2022 Nov 26. Z Med Phys. 2023. PMID: 36446691 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Production and separation of positron emitters for hadron therapy at FRS-Cave M.Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res B. 2023 Aug;541:114-116. doi: 10.1016/j.nimb.2023.04.026. Epub 2023 May 19. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res B. 2023. PMID: 37265512 Free PMC article.
-
Quasi-real-time range monitoring by in-beam PET: a case for 15O.Sci Rep. 2023 Nov 1;13(1):18788. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-45122-2. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37914762 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

