Psychosocial determinants of healthcare personnel's willingness to carry real-time locating system tags during daily inpatient care in hospital managing COVID-19 patients: insights from a mixed-methods analysis
- PMID: 34505000
- PMCID: PMC7928885
- DOI: 10.1093/jamiaopen/ooaa072
Psychosocial determinants of healthcare personnel's willingness to carry real-time locating system tags during daily inpatient care in hospital managing COVID-19 patients: insights from a mixed-methods analysis
Abstract
Objective: Real-time locating systems (RTLS) enable contact tracing and hand hygiene reminders, to improve hospital safety. Successful implementation requires healthcare personnel (HCP) to carry RTLS tags continuously. We assessed for determinants of HCP's willingness to use RTLS tags during routine inpatient care, and evaluated concerns using mixed-methods analysis.
Materials and methods: We conducted a cross-sectional study in the 330-bed purpose-built National Centre for Infectious Diseases in Singapore, from January 15 through February 4, 2020. The anonymous survey comprised 24 questions based on constructs from behavioral models and an open-ended question. Principal component analysis was performed to derive the latent factor structure applied in the multivariable logistic regression analysis. Concerns were analyzed using thematic analysis.
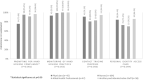
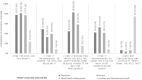
Results: Of 260 HCP (nurses [40.8%], ancillary and administrative staff [23.1%], allied health professionals [18.5%], and physicians [17.7%]), 75% were willing to use the RTLS tag. After adjusting for age, gender, healthcare professional group, and duration of practice, the acceptance of the use of the RTLS tag (adjusted OR 11.28 [95% CI 4.39-29.00], P < .001) was highly associated with the willingness to use the RTLS tag. HCP who perceived the tag to be easy to use (adjusted OR 2.80 [95% CI 1.37-5.72], P = .005), were also more willing to use the tag. HCP were willing to carry the RTLS tag for the purpose of contact tracing despite privacy concerns.
Conclusion: More communications on the intentions and data protection standards of the RTLS, and accessory enhancements for HCP's convenient and sustained use of the RTLS tag are crucial, to optimize RTLS's usefulness during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Keywords: contact tracing; hand hygiene; healthcare personnel; real-time locating system; technology acceptance.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the American Medical Informatics Association.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Performance of Digital Contact Tracing Tools for COVID-19 Response in Singapore: Cross-Sectional Study.JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2020 Oct 29;8(10):e23148. doi: 10.2196/23148. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2020. PMID: 33006944 Free PMC article.
-
Use of a Real-Time Locating System for Contact Tracing of Health Care Workers During the COVID-19 Pandemic at an Infectious Disease Center in Singapore: Validation Study.J Med Internet Res. 2020 May 26;22(5):e19437. doi: 10.2196/19437. J Med Internet Res. 2020. PMID: 32412416 Free PMC article.
-
The Potential Role of an Adjunctive Real-Time Locating System in Preventing Secondary Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in a Hospital Environment: Retrospective Case-Control Study.J Med Internet Res. 2022 Oct 18;24(10):e41395. doi: 10.2196/41395. J Med Internet Res. 2022. PMID: 36197844 Free PMC article.
-
Real-time locating systems (RTLS) in healthcare: a condensed primer.Int J Health Geogr. 2012 Jun 28;11:25. doi: 10.1186/1476-072X-11-25. Int J Health Geogr. 2012. PMID: 22741760 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Real-time location systems technology in the care of older adults with cognitive impairment living in residential care: A scoping review.Front Psychiatry. 2022 Nov 10;13:1038008. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.1038008. eCollection 2022. Front Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 36440422 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Antecedents predicting digital contact tracing acceptance: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2023 Oct 11;23(1):212. doi: 10.1186/s12911-023-02313-1. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2023. PMID: 37821864 Free PMC article.
References
-
- The Insight Partners. RTLS for Healthcare Market to 2027 - Global Analysis and Forecasts by Technology; Facility Type; Application and Geography. 2019: 165.
-
- Camacho-Cogollo JE, Bonet I, Iadanza E.. Chapter 4 - RFID technology in health care In: Iadanza E, ed. Clinical Engineering Handbook. 2nd ed.Academic Press; 2020: 33–41.
-
- Yao W, Chu C-H, Li Z.. The adoption and implementation of RFID technologies in healthcare: a literature review. J Med Syst 2012; 36 (6): 3507–25. - PubMed
-
- Oztekin A, Pajouh FM, Delen D, et al.An RFID network design methodology for asset tracking in healthcare. Decis Support Syst 2010; 49 (1): 100–9.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
