Cosmic Ray Background Removal With Deep Neural Networks in SBND
- PMID: 34505055
- PMCID: PMC8421797
- DOI: 10.3389/frai.2021.649917
Cosmic Ray Background Removal With Deep Neural Networks in SBND
Abstract
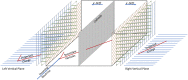
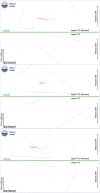
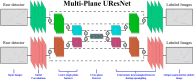
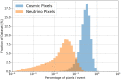
In liquid argon time projection chambers exposed to neutrino beams and running on or near surface levels, cosmic muons, and other cosmic particles are incident on the detectors while a single neutrino-induced event is being recorded. In practice, this means that data from surface liquid argon time projection chambers will be dominated by cosmic particles, both as a source of event triggers and as the majority of the particle count in true neutrino-triggered events. In this work, we demonstrate a novel application of deep learning techniques to remove these background particles by applying deep learning on full detector images from the SBND detector, the near detector in the Fermilab Short-Baseline Neutrino Program. We use this technique to identify, on a pixel-by-pixel level, whether recorded activity originated from cosmic particles or neutrino interactions.
Keywords: SBN program; SBND; UNet; deep learning; liquid Ar detectors; neutrino physics.
Copyright © 2021 Acciarri, Adams, Andreopoulos, Asaadi, Babicz, Backhouse, Badgett, Bagby, Barker, Basque, Bazetto, Betancourt, Bhanderi, Bhat, Bonifazi, Brailsford, Brandt, Brooks, Carneiro, Chen, Chen, Chisnall, Crespo-Anadón, Cristaldo, Cuesta, de Icaza Astiz, De Roeck, de Sá Pereira, Del Tutto, Di Benedetto, Ereditato, Evans, Ezeribe, Fitzpatrick, Fleming, Foreman, Franco, Furic, Furmanski, Gao, Garcia-Gamez, Frandini, Ge, Gil-Botella, Gollapinni, Goodwin, Green, Griffith, Guenette, Guzowski, Ham, Henzerling, Holin, Howard, Jones, Kalra, Karagiorgi, Kashur, Ketchum, Kim, Kudryavtsev, Larkin, Lay, Lepetic, Littlejohn, Louis, Machado, Malek, Mardsen, Mariani, Marinho, Mastbaum, Mavrokoridis, McConkey, Meddage, Méndez, Mettler, Mistry, Mogan, Molina, Mooney, Mora, Moura, Mousseau, Navrer-Agasson, Nicolas-Arnaldos, Nowak, Palamara, Pandey, Pater, Paulucci, Pimentel, Psihas, Putnam, Qian, Raguzin, Ray, Reggiani-Guzzo, Rivera, Roda, Ross-Lonergan, Scanavini, Scarff, Schmitz, Schukraft, Segreto, Soares Nunes, Soderberg, Söldner-Rembold, Spitz, Spooner, Stancari, Stenico, Szelc, Tang, Tena Vidal, Torretta, Toups, Touramanis, Tripathi, Tufanli, Tyley, Valdiviesso, Worcester, Worcester, Yarbrough, Yu, Zamorano, Zennamo and Zglam.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



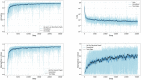
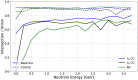
References
-
- Abadi M., Agarwal A., Barham P., Brevdo E., Chen Z., Citro C., et al. . (2015). TensorFlow: Large-Scale Machine Learning on Heterogeneous Systems. Available online at: tensorflow.org.
-
- Abi B., Acciarri R., Acero M. A., Adamowski M., Adams C., Adams D., et al. . (2018a). The DUNE far detector interim design report volume 1: physics, technology and strategies. arXiv:1807.10334. 10.2172/1529363 - DOI
-
- Abi B., Acciarri R., Acero M. A., Adamowski M., Adams C., Adams D., et al. . (2018b). The DUNE far detector interim design report, volume 2: single-phase module. arXiv:1807.10327. 10.2172/1529362 - DOI
-
- Abi B., Acciarri R., Acero M. A., Adamowski M., Adams C., Adams D., et al. . (2018c). The DUNE far detector interim design report, volume 3: dual-phase module. arXiv:1807.10340. 10.2172/1529361 - DOI
-
- Abi B., Acciarri R., Acero M. A., Adamowski M., Adams C., Adams D. L., et al. . (2017). The Single-Phase ProtoDUNE Technical Design Report Proto DUNE. 10.2172/1366526 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

