Improved precision of noise estimation in CT with a volume-based approach
- PMID: 34505172
- PMCID: PMC8429536
- DOI: 10.1186/s41747-021-00237-x
Improved precision of noise estimation in CT with a volume-based approach
Abstract
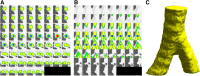
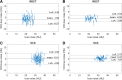
Assessment of image noise is a relevant issue in computed tomography (CT). Noise is routinely measured by the standard deviation of density values (Hounsfield units, HU) within a circular region of interest (ROI). We explored the effect of a spherical volume of interest (VOI) on noise measurements. Forty-nine chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients underwent CT with clinical protocol (regular dose [RD], volumetric CT dose index [CTDIvol] 3.04 mGy, 64-slice unit), and ultra-low dose (ULD) protocol (median CTDIvol 0.38 mGy, dual-source unit). Noise was measured in 27 1-cm2 ROIs and 27 0.75-cm3 VOIs inside the trachea. Median true noise was 21 HU (range 17-29) for RD-CT and 33 HU (26-39) for ULD-CT. The VOI approach resulted in a lower mean distance between limits of agreement compared to ROI: 5.9 versus 10.0 HU for RD-CT (-40%); 4.7 versus 9.9 HU for ULD-CT (-53%). Mean systematic bias barely changed: -1.6 versus -0.9HU for RD-CT; 0.0 to 0.4HU for ULD-CT. The average measurement time was 6.8 s (ROI) versus 9.7 (VOI), independent of dose level. For chest CT, measuring noise with a VOI-based instead of a ROI-based approach reduces variability by 40-53%, without a relevant effect on systematic bias and measurement time.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02477397.
Keywords: Data accuracy; Noise; Pulmonary disease (chronic obstructive); Thorax; Tomography (x-ray computed).
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
RV is supported by an institutional grant from Siemens Healthineers. The other authors have no competing interests to be declared.
Figures

References
-
- European Commission (2000) European guidelines on quality criteria for CT, available at https://op.europa.eu/s/n8PM, archived at http://web.archive.org/web/20210225144451/https://op.europa.eu/o/opporta.... Office for Official Publications of the European Communities
-
- den Harder AM, de Boer E, Lagerweij SJ, Boomsma MF, Schilham AMR, Willemink MJ, Milles J, Leiner T, Budde RPJ, de Jong PA. Emphysema quantification using chest CT: influence of radiation dose reduction and reconstruction technique. Eur Radiol Exp. 2018;2:30. doi: 10.1186/s41747-018-0064-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
